Introduction
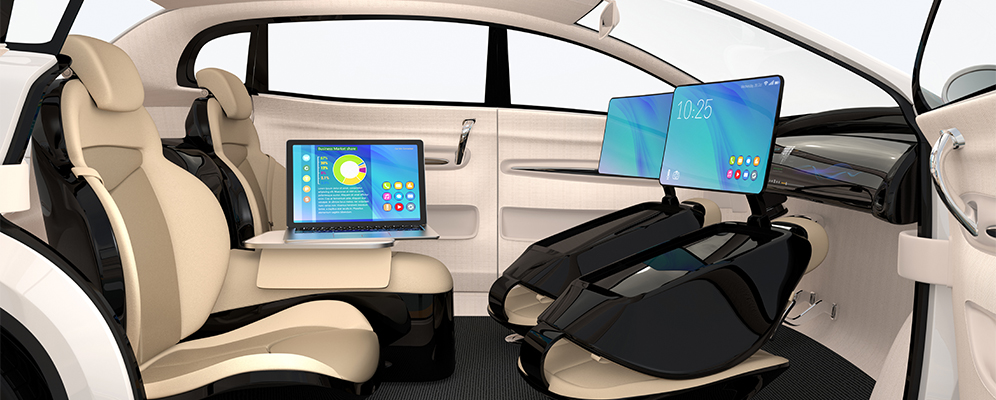
The vehicle interiors are expected to witness a shift from traditional design to innovative concepts based on customer needs to improve user experience. With no driver required for autonomous vehicles, the in-vehicle experience is expected to witness a significant change. Passengers will have more freedom to relax, get entertained, and do work while traveling.
Before getting into the interiors of an autonomous vehicle, it is important to look at the market in terms of its demand and current state.
Currently, the majority of the new vehicles in the market are level 1 and level 2 autonomous cars with limited driver assistance capability. Most of the low-range and mid-range cars in the developing countries are fully manual-operated. Hence, we can look at fully (level 4 and 5) autonomous driving post-2030 (Refer to Exhibit 1).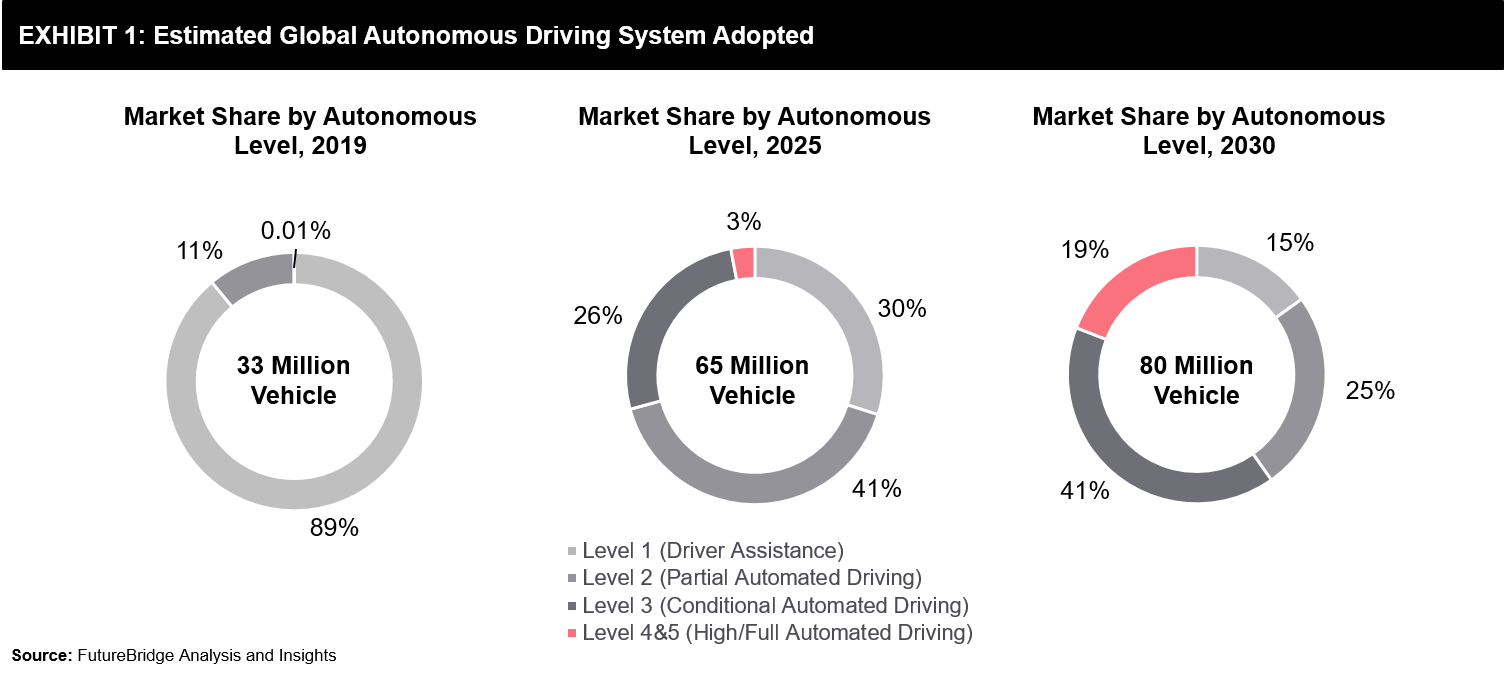
With fully autonomous driving making its way towards reality this blog will look to highlight the following to take a look into the autonomous interiors and the changes expected in the ecosystem:
- What is the current situation of autonomous interiors in terms of the concepts being developed across the leading players in the mobility ecosystem?
- What are the changes/business models expected in the autonomous mobility (level 5), which would bring a revolution in the autonomous interiors?
- What is expected in the future of interiors once fully autonomous vehicles become a reality?
Current Scenario
The journey towards autonomous interiors is not new. OEMs have been designing and working on the different concepts concerning space, comfort, convenience, and safety over time. Currently, there are OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers working towards innovating the interiors based on future customer preferences.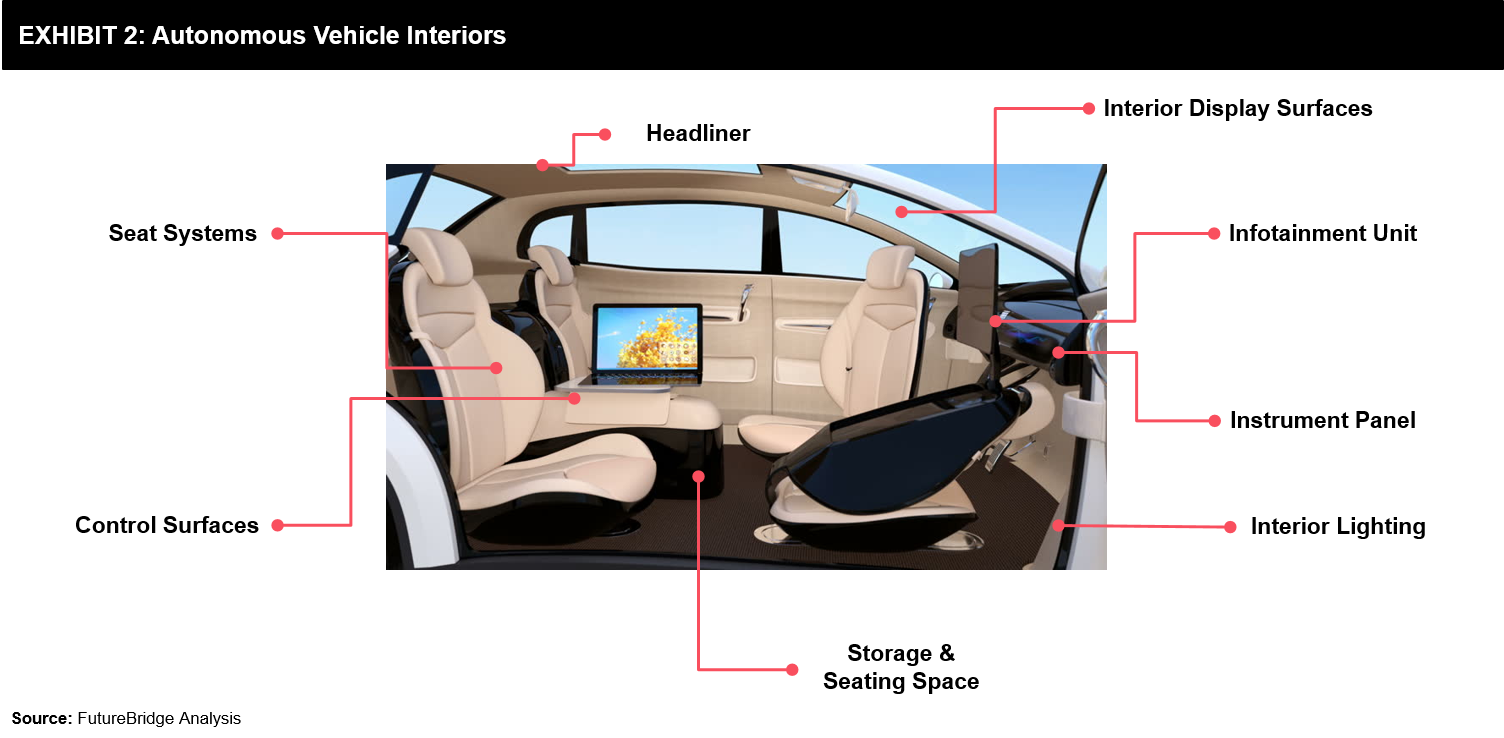
Within autonomous interiors (Refer to Exhibit 2), seating will be a crucial area where several changes are expected. Greater number of adjustment features in the seat, a higher degree of movement and rotation are just a few of the areas, which are currently under focus.
This article looked into three key areas of autonomous interiors, namely storage & seating space, instrument panels, and infotainment unit.
Highlighted below are some examples of innovations across seating concepts.
Evolving seating concepts
![]() Innovative Seating Concept AI18 for Level 4 ride-sharing vehicles and AI17 for privately-owned vehicles
Innovative Seating Concept AI18 for Level 4 ride-sharing vehicles and AI17 for privately-owned vehicles
Adient, a supplier to automotive OEMs, has developed two seating concepts one for ride-sharing and the other for private vehicles.
 For ride-sharing autonomous vehicles: The company has developed a concept AI18 for level 4 ride-sharing vehicles. In it, along with safety and comfort, the intelligent front seat monitors the seating position of the driver and the occupant; also, it measures their heart and respiration levels to assess their stress levels and provide solutions, whenever required.
For ride-sharing autonomous vehicles: The company has developed a concept AI18 for level 4 ride-sharing vehicles. In it, along with safety and comfort, the intelligent front seat monitors the seating position of the driver and the occupant; also, it measures their heart and respiration levels to assess their stress levels and provide solutions, whenever required.
- For privately-ow
 ned autonomous vehicles:
ned autonomous vehicles:
The company has also developed a concept AI17 for private-owned vehicles. Here, the interior has been developed focusing on consumers and the interactions that they can have in the vehicle. It has an adaptive seating feature, which rotates 15 degrees inwards, enabling comfort and easy consumer interaction. The seats also greet the passengers, while entering the vehicle by rotating outwards.
![]() New Seating System for flexible and collaborative interior for ride-sharing in autonomous vehicles
New Seating System for flexible and collaborative interior for ride-sharing in autonomous vehicles
Magna, a supplier to automotive OEMs, has built on a concept, which includes three specific configurations for flexible seating intended for cargo carrying, long road trips, and autonomous ride-sharing:
 Cargo mode: Vehicle’s three rows of seats slide to the front of the vehicle on rails and nest under the instrument panel to create a large cargo area at the back.
Cargo mode: Vehicle’s three rows of seats slide to the front of the vehicle on rails and nest under the instrument panel to create a large cargo area at the back.- Campfire seating mode: Seats slide and swivel on long rails around the periphery of the interior, so occupants face each other, with three on each side and two seats at the front and rear.
- Autonomous ride-sharing mode: Seats swivel and reverse on power long rails; also, there are seat signals that indicate which seats are available for ride-sharing.
![]() New Seating System for flexible and collaborative interior for ride-sharing in autonomous vehicles
New Seating System for flexible and collaborative interior for ride-sharing in autonomous vehicles
Hyundai Motor Group, a joint venture between Hyundai Motor Group Hyundai, Kia, and Genesis, has unveiled the concept for second-generation seats, incorporating the generative design. In this, the venture has focused on luxurious features such as a super-relaxation mode for the rear passengers. The seats are made for three different modes: normal, communication (where the front seats rotate 15 degrees inward), and super-relaxation. In addition to this, there is an easy-access mode that ensures easy entry and exit i.e.; the seats can swivel outwards.
Transforming Instrument Panels
With a change is seating arrangement, innovations are going around the instrument panels as well. Examples of some companies who are developing these concepts are as follows:
![]() XiM17 Autonomous interiors with lounge, meeting, family and driving mode with a focus on the instrument panel
XiM17 Autonomous interiors with lounge, meeting, family and driving mode with a focus on the instrument panel
 Yanfeng Automotive Interiors, one of the leading global providers in automotive interiors, in 2017, demonstrated an autonomous interior concept with four different modes, namely lounge, meeting, family, and driving, where the company has mainly focused on the instrument panel.
Yanfeng Automotive Interiors, one of the leading global providers in automotive interiors, in 2017, demonstrated an autonomous interior concept with four different modes, namely lounge, meeting, family, and driving, where the company has mainly focused on the instrument panel.
Along with swing back seats and storage space, the company has incorporated a specific focus on the rear seats. A unique feature combines the front and rear seats and ensures that the rear passengers can view the large display in the instrument panel.
Also, along with a large overhead screen and focus on interior lighting, the company has ensured a large storage space in the instrument panel. The storage is placed at the center of the instrument panel and also has a sliding opening, which allows easy access for the passengers.
![]() Morphing Instrument Panel can also be called as the adaptive instrument panel
Morphing Instrument Panel can also be called as the adaptive instrument panel
 Faurecia, a France-based global automotive supplier, has unveiled an innovative instrument panel concept, where the panel adapts to the changes, as per driving mode.
Faurecia, a France-based global automotive supplier, has unveiled an innovative instrument panel concept, where the panel adapts to the changes, as per driving mode.
In the normal driving mode, the driver can see the panel, which is useful for navigation, ensuring road and safety information.
As soon as the autonomous mode is switched on, the display glides and moves to the center of the panel. This ensures the display is visible for all passengers, as the screen also adapts and becomes large.
Evolving Infotainment Unit
The connected vehicle market’s rapid market growth has propelled OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers to focus on in-car infotainment. Three key factors are driving the in-vehicle customer experience to entertain passengers:
- Increase in customer demand for a better experience
- Increase in the usage of innovative technologies like AI, IoT, and 5G
- The arrival of level 3 autonomy and progress towards level 4 and 5
One of the open questions is how the in-car infotainment will change with autonomous driving? OEMs are coming with solutions where they are developing infotainment systems based on each passenger traveling inside the vehicle. Some key areas which are critical for OEMs to investigate include:
- Human Machine Interface: In this head-up-displays (HUDs) will play a crucial role, as the display in front of the driver or co-passengers will play a vital role in last-mile navigation and, more importantly, alert in case of emergency. OEMs (such as Mercedes, Volvo, and BMW) also have integrated the HUDs with in-vehicle infotainment.
- In-vehicle Commerce: Increasingly customers are interested in connected commerce where they can shop, buy, and eat inside the car. In-vehicle commerce shows promising prospects and is a big market opportunity for OEMs and is expected to grow rapidly.
- Others: In addition to this, navigation, video streaming, music, gaming, and in-car voice assistants are other vital areas that OEMs are working on.
Innovation is the key to autonomous driving, and it will be worthwhile to mention the leading technologically advanced OEMs and their recent innovations with respect to infotainment systems.
![]() Mercedes 2021 S-Class MBUX Infotainment System
Mercedes 2021 S-Class MBUX Infotainment System
Mercedes, a leading OEM, has unveiled its new flagship S-Class MBUX Infotainment System, where the passengers in the rear can enjoy the same entertainment as that in the front. Each passenger can use their personalized entertainment system. It also has a new 3D driver display, which allows a special view and a three-dimensional effect is ensured without the usage of a 3D glass. The vehicle also has an Augmented HUD for driver assistance, which projects navigation in the windshield.
 The BMW i Interaction Ease
The BMW i Interaction Ease
BMW, another leading OEM, has unveiled the concept of ‘i Interaction EASE’. In this, along with greeting the passenger in an autonomous vehicle, they can interact with the vehicle using a new type of gesture control, the gaze detection system. The passenger need not learn various commands. The vehicle using intelligent AI adapts itself to the exterior environment and provides the passenger with various options of having coffee, food, etc. A spoken and gesture command can be given to the subject, as soon as the passenger finds something interesting inside the vehicle, as per the exterior environment. There are three modes that the passenger can choose from – Explore, Entertain, and Ease.
![]() The Bentley EXP 100 GT
The Bentley EXP 100 GT
 Bentley, a leading automotive OEM, has unveiled a concept, where the vehicle exterior is fitted with cameras to capture pictures and memories of previous drives. The passenger traveling can view the earlier memorable rides in the smart glass window of the vehicle during autonomous mode when on the urban commute or whenever required. The vehicle can also dispense cartridges filled with snacks, purified water, travel items, and clean clothes through a simple hand gesture.
Bentley, a leading automotive OEM, has unveiled a concept, where the vehicle exterior is fitted with cameras to capture pictures and memories of previous drives. The passenger traveling can view the earlier memorable rides in the smart glass window of the vehicle during autonomous mode when on the urban commute or whenever required. The vehicle can also dispense cartridges filled with snacks, purified water, travel items, and clean clothes through a simple hand gesture.
 In terms of safety, the vehicle can also sense the driver’s mood by monitoring health indicators like blood pressure and head gestures and accordingly adjust the lighting, ambiance, and driving-style of the vehicle.
In terms of safety, the vehicle can also sense the driver’s mood by monitoring health indicators like blood pressure and head gestures and accordingly adjust the lighting, ambiance, and driving-style of the vehicle.
Autonomous vehicles will also create opportunities in the form of novel use cases of the vehicles, many times, even leading to novel business models. These new use cases and business models will have a direct and indirect impact on the autonomous vehicle interiors, depending on the specific vehicle applications.
New Business Models
The new business models can be based on numerous use cases and applications depending on customer needs and preferences. Looking into some of the concepts developed by players like Toyota in their e-Palette Concept, and other OEMs, FutureBridge predicts that the future will not only be ‘living on wheels’ it will be ‘business on wheels’, as well.
A Mobile Restaurant
In a level 5 autonomy scenario, mobile restaurants can be a new use case for the vehicle. In this, the passengers can pre-book their time slots depending on their requirements concerning food, interiors, time, and location of having a meal. There will be multiple challenges that the mobile restaurant will have to deal with, for instance, whether the meal will be prepared in advance or it has to be a live kitchen depending on which the vehicle interior has to be modified accordingly. Also, the storage and seating arrangement has to be focused on, where the vehicle interiors will play a key role.
A Moving Accommodation/Hotel
In this scenario, the autonomous vehicle can be moving accommodation or hotel. A passenger can move destinations inside a vehicle with all amenities inside the vehicle. This model will be beneficial for the passengers, saving time and indirectly cost for the traveler. Again, vehicle interiors will play an important role, as it will be necessary to provide luxury depending on the passenger’s budget, similar to what one gets in a hotel or accommodation.
A Hospital on the Wheels
Moving hospitals can be beneficial in case of emergencies. This model can be challenging in terms of the doctors, patients, and hospital equipment to be incorporated inside a vehicle. However, with the progress of technology, this can be a reality in the future. The vehicle interiors are to be designed with the utmost care, as this will ensure the patients are well treated, and fully equipped with all the necessary equipment.
A Walking Fab-lab
Fab-labs are interesting when there is no mass-scale production involved. This model can be incorporated in autonomous vehicles to ensure the production is done within the vehicle. For instance, a prototype can be prepared while the vehicle moves and collects various essential accessories required to manufacture it. Once done, it can be delivered to the desired location.
A Moving Lounge
It can well be imagined a lounge picking passenger(s) from a specific location or right at their doorstep and providing them with a luxury experience. The lounge can be used for multiple purposes, including a movie theatre, a gaming experience, or even relaxing for some time.
A Physical E-Commerce at your Door Step
In this scenario, a mobile autonomous vehicle is imagined that can arrive at consumers’ doorstep with products that they want to buy. This will also address the issue of product recalls for the e-commerce industry. The customer can have a real e-commerce experience at his/her doorstep without traveling.
Interiors to be Crucial in the Long-term
All the above business models are concepts to be built in the long-term and may take more than 15–20 years to become a reality, or there can also be a case of some of them getting adopted, while others are scrapped due to business challenges. All these models hint at one thing very clearly that is the vehicle interior has to modify as per business needs and requirements. For instance, a hospital set-up will be completely different from a restaurant or physical e-commerce.
Conclusion – Looking at the Future
FutureBridge expects increasing collaborations (Exhibit 3) between various players across the autonomous automotive interiors ecosystem.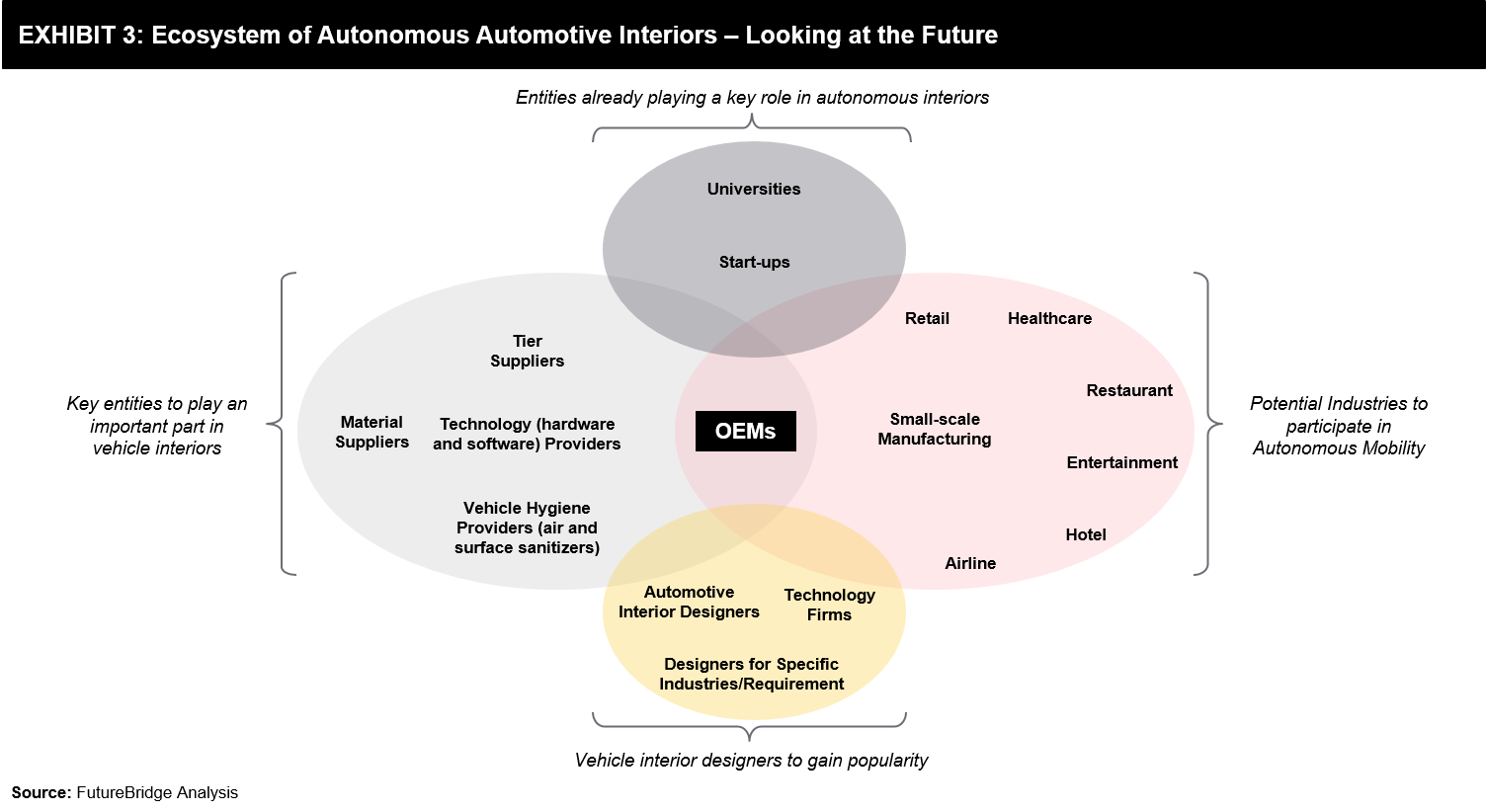
It is very clear that OEMs mostly will take the ‘center stage’ in the vehicle interior ecosystem. Tier 1 suppliers and material suppliers will also play a crucial role in the vehicle interior value chain. However, there will be players from outside the conventional value chain as well, that will have a role to play in the autonomous vehicle interiors opportunity. For instance, while Sony’s unveiling of its first concept car Vision-S does not indicate its entry into the car market, it showcases its capabilities in cameras, sensors, and touch screens.
Therefore, the incumbents across the value chain need to assess which kind of collaborations they should forge with players that are not traditional automotive value chain players.
References
- https://www.adient.com/advancements/ai18
- https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2018/12/10/1664558/0/en/Magna-Reveals-New-Seating-Ecosystem-Designed-to-Offer-More-Flexible-Collaborative-Interior.html
- https://news.hyundaimotorgroup.com/Article/We-look-at-passenger-seats-for-the-age-of-autonomous-driving
- https://www.yfai.com/en/xim17
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/joshmax/2018/01/19/faurecias-auto-cockpits-of-the-future-dazzle-at-ces/#674f06554e1f
- https://www.autonomousvehicletech.com/articles/2262-bmw-group-displays-mobility-solutions
- https://global.toyota/en/newsroom/corporate/29933371.html
- https://www.autocarindia.com/car-news/2021-mercedes-benz-s-class-mbux-system-details-revealed-417934
- https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2019/07/11/bentley-unveils-self-driving-concept-car-will-tell-bad-mood/
- https://www.verdict.co.uk/interior-design/
- https://360.here.com/5-predictions-for-the-future-of-in-car-leisure-entertainment



































