Introduction
In-car payment systems are one of the most prominent Human-Machine-Interface trends in the mobility industry with rapid growth in autonomous and connected vehicles (refer to Exhibit 1). In addition, 5G and improved Wi-Fi connectivity are also expected to increase the adoption of in-car payment systems.
Payment functionality in vehicles are enabled through:
- RFID tags that can send payment data over-the-air
- Embedded BLE hardware modules that can transmit data at a higher range
The cost of embedded systems is higher than integrated systems (such as RIFD); however, the former provides real-time solutions. Embedded systems have their own operating units, which, in turn, reduce the risk of payment failure. There are still some challenges with in-car payment systems, as personal data and financial information (such as card number, PIN, and CVV) may be compromised due to cyber-attacks. For instance, there was a technical issue in the dashboard of Chryslers, which had allowed hackers to disable the vehicle; Fiat had to recall more than a million vehicles owing to this issue.
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) will also be a critical factor that will contribute towards the growth of the in-car payment systems. Payment systems embedded in vehicles will be enabled by ISPs, which will help provide a seamless customer experience.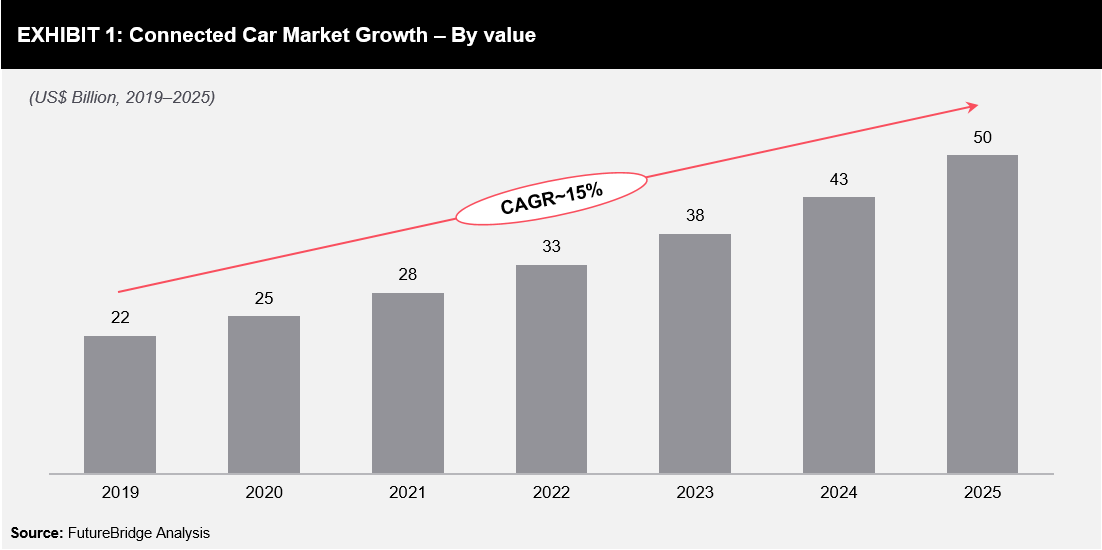
Key Initiatives for In-vehicle Payment Solutions
The concept of in-car payment systems is not very new; however, there has been an increased penetration since 2017 (refer to Exhibit 2). Companies such as General Motors, Volkswagen, and ZF Friedrichshafen have undertaken initiatives towards customer excellence and partnered with entities in the value chain to offer seamless in-car payment solutions experience.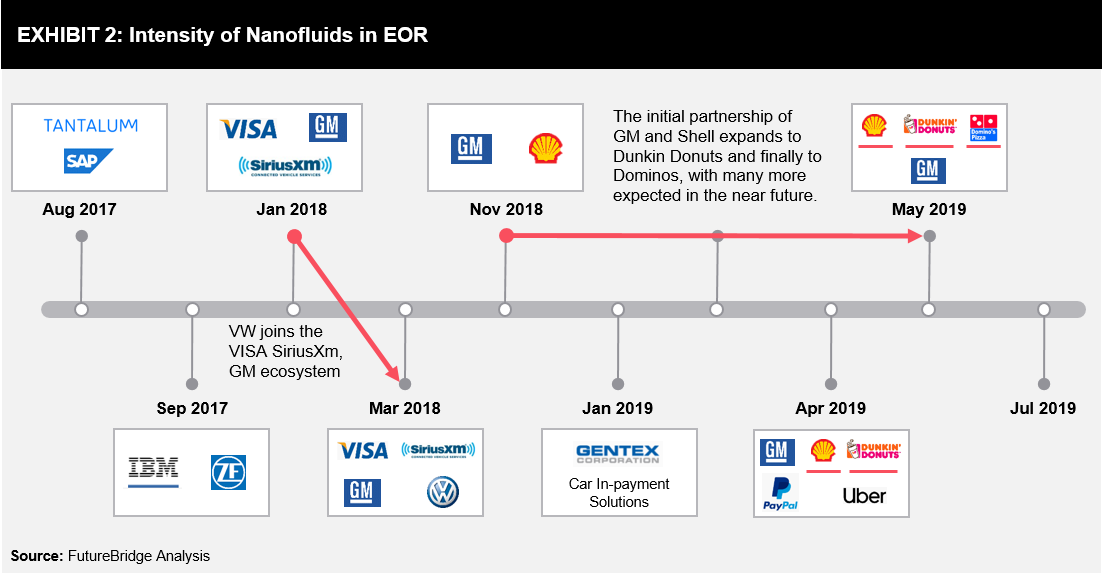
Some other latest (in 2019) prominent initiatives are listed as follows:
In 2019, Hyundai partnered with Xevo (a leader in connected-car and automotive telematics technologies) for telematics solutions in the US and Europe.
- The platform will provide Hyundai vehicles with access to engage and interact with favorite merchant brands and services through an easy-to-use interface on the in-vehicle touchscreen and mobile app.
- The offerings will include fuel, parking, and dining, as well as the digital payment feature.
- Merchants can promote their featured products by prompting touchscreen notifications on the driver’s screen.
In 2019, Telenav (a wireless location-based services corporation) partnered with Microsoft to integrate its intelligent connected-car solutions suite with the Microsoft Connected Vehicle Platform (MCVP).
- The platform combines cloud and edge services with a partner network that helps companies accelerate their development of connected vehicle solutions.
- In this partnership, along with other services such as OTA and telematics, Telenav is working on connected cloud and in-vehicle services for automotive infotainment, in-car commerce, and navigation.
In 2019, FCA launched an in-vehicle U-connect market commerce platform (refer to Exhibit 3), which was developed in partnership with Seattle-based Xevo.
- Customers can order food, save money on fuel purchases, and make dinner reservations via a touchscreen.
- It also allows drivers to locate and pay for nearby parking and schedule service appointments at FCA US dealerships.
Brand partners include Shell, Domino’s, Park Whiz, and Yelp Reservations.
In 2019, Jaguar Land Rover tested a new Smart Wallet technology that will pay users in cryptocurrency for sharing data, such as road and traffic conditions, with authorities and navigation service providers.
- Smart Wallet will alert drivers on traffic conditions and offer alternate routes, thereby reducing fuel consumption and vehicle emissions.
- Users sharing this data will be rewarded with credits, which could be redeemed for rewards, paying tolls, and parking fees or for charging electric vehicles.
- Technology is being tested at their facility in Shannon, Ireland, where several cars, including the F-Pace and the Velar, are equipped with Smart Wallet.
Ecosystem of Payment System Providers
Key participants in the payment systems ecosystem include platform, processing, account, connection, messaging, and settlement providers (refer to Exhibit 4). These participants abide by the regulations and guidelines prevalent in their respective geographies and are responsible for handling transactions till settlement.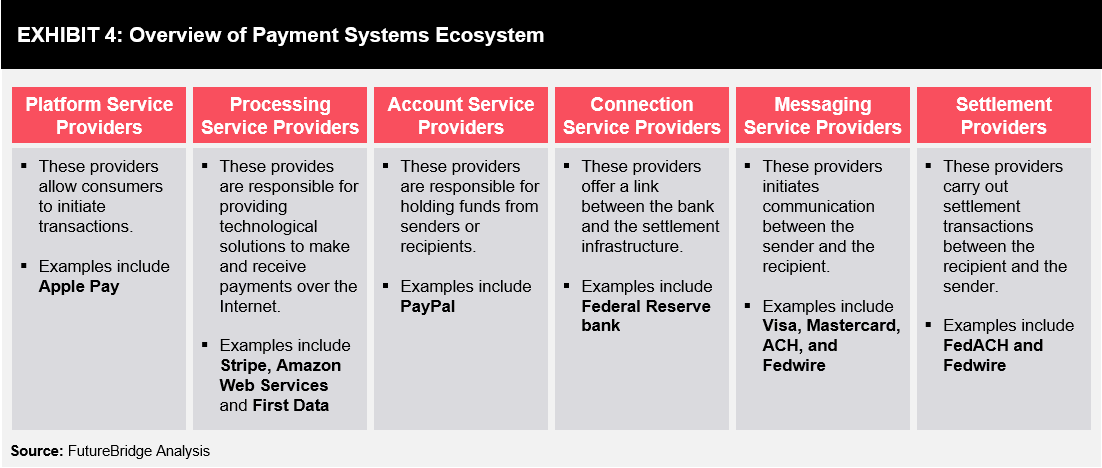
Mostly, banks govern payment systems within individual countries. However, with the introduction of the revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) by 2020 in the EU, there will be changes in the ecosystem with more competition, innovation, and transparency within the payments sector.
PSD2 ensures increasing customer protection and competition; this directive enables bank customers to use third-party providers (fintech companies) for managing their finances. Banks can no longer hold customer account information and will have to share it with third-party providers, thereby opening the doors for third-party providers to innovate their financial services. Banks will face stiff competition from third-party providers.
In addition, the new regulation opens up two key approaches:
- Payment initiation through Payment Initiation Providers who can initiate payments on behalf of the user
- Account Information Service Providers, who have access to the account information of bank customers
- These providers can have consolidated information of a single user from multiple bank accounts and will be able to analyze customer spending behavior.
While consumers–individuals/businesses will be the real gainers due to regulations such as PSD2, it will allow fintech companies to establish their market in the near-term (1–2 years). Banks will have to strategize initiatives to sustain in this stiff competitive environment.
Future Ahead
The market for in-car payment solutions is expected to increase significantly worldwide with a rise in the number of connected cars. Various players in the traditional ecosystem are identifying different avenues that could help enhance their market share either through revenue generation, product expansion, or customer loyalty.
According to estimates, the in-vehicle commerce market holds >USD200 billion market opportunity, which is expected to grow significantly in the next 3–5 years. Some of the key activities (refer to Exhibit 5) among consumers include ordering coffee, searching for parking lots, ordering food & grocery, and searching for a gas station. Fuel/gas filling is expected to be the highest spend and most popular in-vehicle commerce activity among commuters, globally.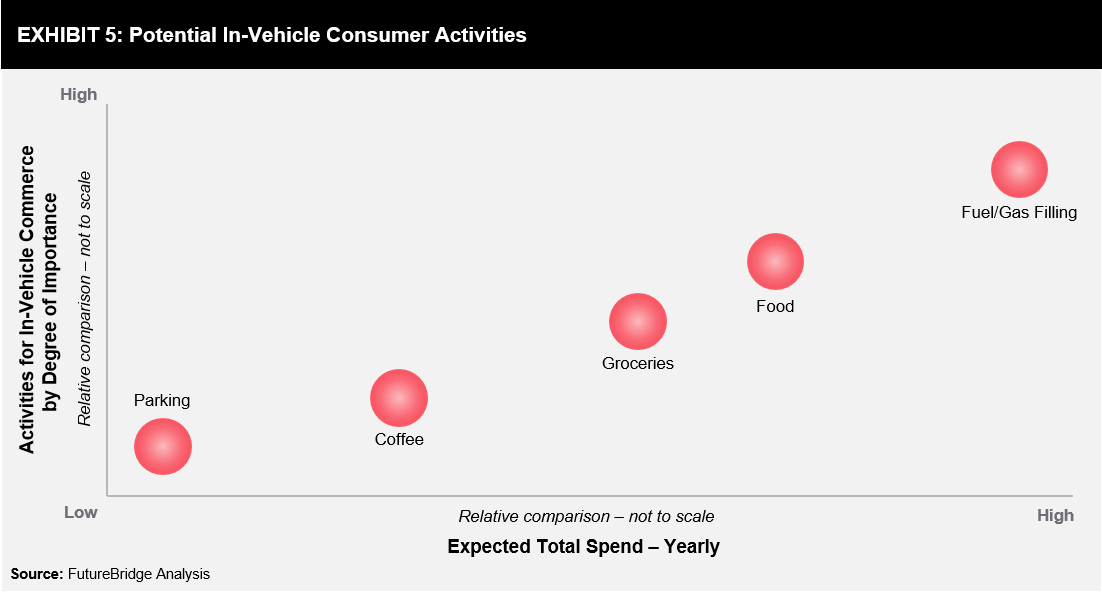
Due to this, significant opportunities are expected across the value chain:
- Payment Service Providers: Payment service providers will have ample opportunities for creating alliances between them and stores, gas stations, etc.
- They will act as an intermediary between retailers, consumers, and fleet operators. This will provide payment service providers with opportunities to create customer-oriented tools. They can act as a helping intermediary for OEMs, advising them on critical aspects of payment features available in the existing vehicles as well as future vehicles.
- They will also have opportunities to consolidate ample data available across multiple systems and functions. This data will be analyzed, which, in turn, will help create and maintain standards, such as authentication, risk modeling, and tokenization.
- OEMs: OEMs will have the opportunity to innovate future vehicles with additional features and attract customers by offering a seamless driving experience.
Need a thought partner?
Share your focus area or question to engage with our Analysts through the Business Objectives service.
Submit My Business ObjectiveOur Clients
Our long-standing clients include some of the worlds leading brands and forward-thinking corporations.
- © 2021 Cheers Interactive (India) Private Limited. All rights reserved. FutureBridge ® is a registered trademark of Cheers Interactive (India) Private Limited.




































