Smartphones Technologies Disrupting Remote Health Monitoring
Listen to this Article
mins | This voice is AI generated.
mins | This voice is AI generated.
The ubiquitous presence of smartphones and internet-of-things (IoT) are encouraging the trend of remote health care monitoring. A study conducted on the analysis of time savings to deliver care through remote monitoring in the US Department of Veterans Affairs showed that an average of 142 minutes per visit was saved. The remote monitoring of blood glucose, electrocardiogram (ECG), and blood pressure are quite common in patients suffering from diabetes and cardiac conditions using point-of-care devices. Traditionally, remote health monitoring was used as conveying patient data through telephone interviews and video conferencing to the healthcare practitioner.
Many companies are working towards developing smartphone-based solutions for the assessment of health and wellness parameters such as vitamin and mineral status, lung function, blood alcohol level, etc. to critical illness conditions such as pregnancy-related complications, infections, respiratory disorders, etc. Several smartphone-based applications and customized attachments/sensors have been introduced for monitoring physiological parameters such as bilirubin content in blood, blood pressure, ECG, ear infection, etc. Although smartphone-based monitoring is a supplementary approach to lab or clinical testing, it can help patients to monitor their health at home with fewer hospital/lab visits, which can significantly improve the quality of life for the patients. It has now evolved to the use of smartphones for at-home monitoring which may be carried out by untrained individuals.
The elements that made smartphones act as monitoring devices are in-built sensors, customized smartphone attachments/ sensors, data handling, processing power, and wireless communication capabilities. There are several monitoring applications present in the market that make use of smartphone in-built sensors such as camera, microphone, accelerometer, etc. Leveraging the sensory capabilities of the smartphone, remote monitoring and self-management of the disease is possible, without incurring any additional cost for lab testing and customized smartphone attachments. The attachments/sensors include electrode pads, reader, ultrasound wand, etc., and a means to interface the attachments/sensors to the smartphone. The attachments/sensors utilize the capabilities of the smartphone in terms of computation and networking. The in-built sensors can be employed as a stand-alone sensing unit or coupled with customized smartphone attachments/ sensors. Refer to Exhibit 1 which represents a few therapeutic areas and monitored parameters based on site of monitoring.
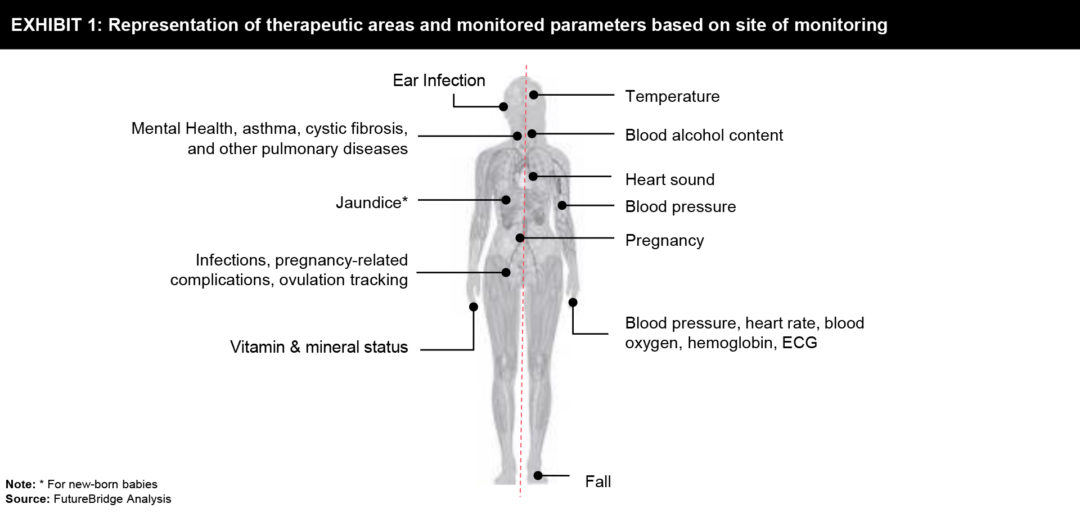

Most of the data handling is done by mobile applications while some of them use cloud computation for faster results. The wireless connectivity to attachments/sensors and networking to the healthcare professional for sharing monitored data are achieved through Bluetooth or the internet. The same channel can be used by the healthcare professional to give instructions to the patient based on the shared health data.
With more than three billion smartphone users in the world, smartphone-based monitoring is the easiest way to reach out to the masses and remote areas. The following benefits/impact of this technology make it widely acceptable:
The major impact of the adoption of smartphone technologies would be on Quality of Life (QoL)
Smartphone technologies, wearable sensors, and smartphone platforms would enable, monitoring the health/vitals of patients/consumers remotely. This would eventually result in – preventive care, well-timed diagnosis, and screening of ailments, and timely treatment. This reduces the rate of hospital visits, hospitalization and so the hospital-induced infections. Collectively all these benefits result in improving the QoL.
The flexibility of diagnosis while on the go and Real-time monitoring has increased its adoption rate
The technology enables patients to monitor the parameters on a real-time basis in non-clinical environments such as home, office, park, and while traveling, etc.
Attributes of cost & time saving, and continuous monitoring along with communication with prescribers make it a compelling proposition
With no cost or minimal cost of the mobile applications or customized attachments/ sensors, frequent visits to the diagnostic labs and healthcare professionals, and wait time can be prevented.
For effective patient care and safety, continuous monitoring of physiological parameters is needed. With the use of the smartphone, monitoring can be done anytime and anywhere, and alerts/ notifications can be communicated to the healthcare professional. Immediate attention can be provided remotely in case of an emergency.
Non-Invasive diagnosis, User-friendly data representation, and comparison/benchmarking tools put it ahead of traditional monitoring systems
Non-invasive at-home monitoring: Collaboration between technology, devices, and diagnostic companies is focusing heavily on the convenience and non-invasiveness of diagnostic tests and monitoring for home care and remote patient management.
Benchmarking: Several monitoring applications collect data from other users and lets the user/care provider benchmark his/her/patient’s health condition.
Visual and auditory representation: The data obtained using traditional monitoring methods were interpretable only by healthcare professionals. While smartphone-based monitored data can be understood by patients as well due to its efficient visual and auditory representation.
A large number of companies are developing smartphone-based diagnostic solutions. Academia is also working on technologies related to non-invasive at-home monitoring using smartphones. Listed in Table 1 are some products/ technologies developed for diagnostics purposes.
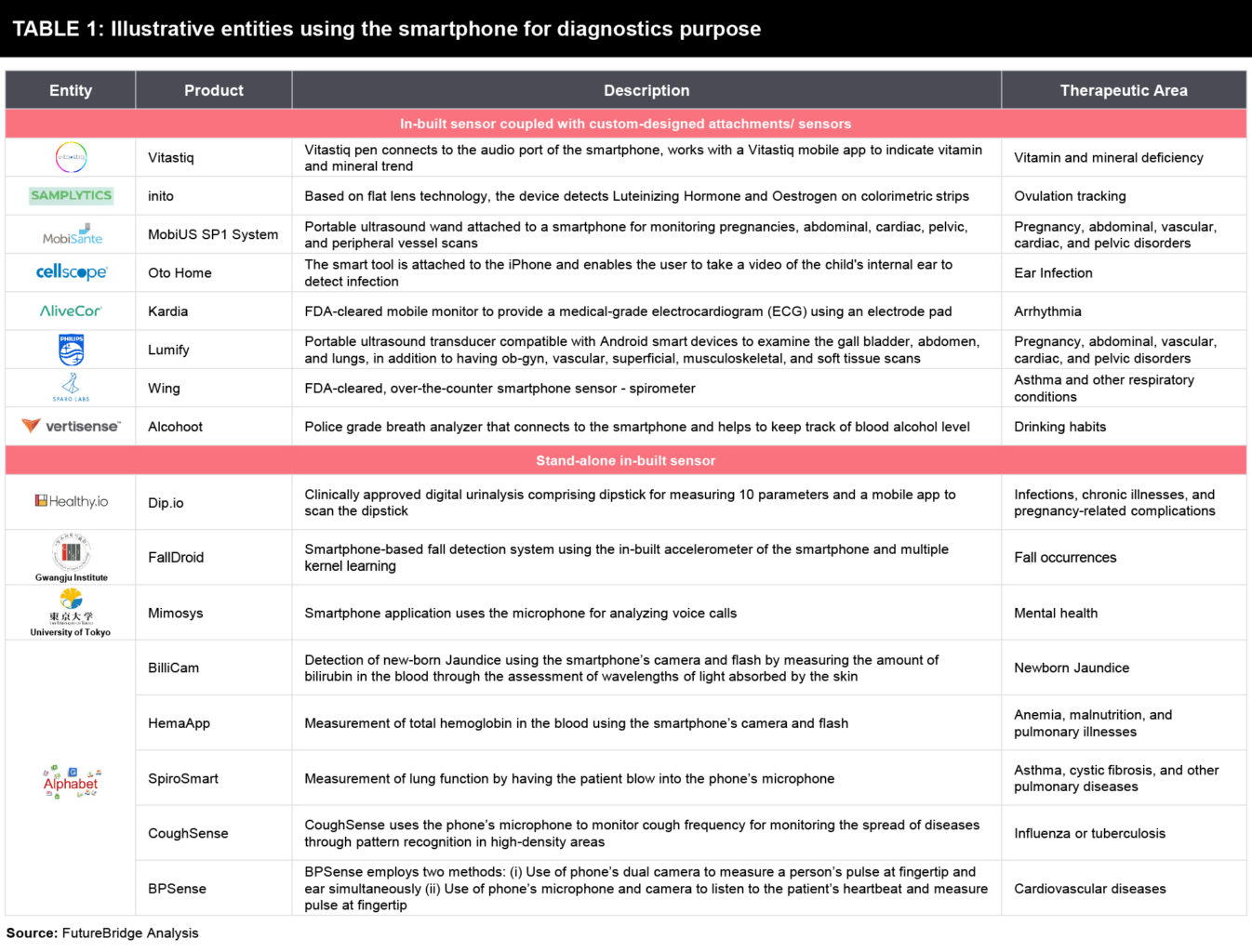

Although the quality of an individual’s life is improved, certain challenges appear as the bottleneck in the success of the technology.
Continuous monitoring at home is an important aspect for critically ill patients which can be solved by smartphone-enabled monitoring. Any potential life-endangering conditions can be averted by monitoring even a slight variation in the physiological parameters. Even, the cost and inconvenience of frequent hospital visits are reduced, thereby improving the quality of life of the patients.
As a part of preventive healthcare, remote monitoring is expected to evolve rigorously in the future decades with technological advancement in sensors and newer ways of monitoring health and wellness parameters. Adding specific sensors to the smartphone may increase the cost of monitoring but will help in increasing the information captured in terms of resolution, accuracy, and precision. The health parameters may range from vital body parameters to vitamin and mineral status, and from ovulation tracking to chronic disease conditions. Many startups such as Vitastiq, Samplytics Technologies, etc. have emerged as innovative solution providers in the domain of healthcare monitoring, while big players such as Alphabet have entered into the domain by acquiring startup Senosis Health. Some companies are also focussing on creating smartphones smarter by incorporating prototype sensors in the smartphones themselves, instead of plug-ins/clip-on. For example, Leman Micro Devices introduced an e-Checkup V-sensor that is built into the back of any e-Checkup enabled smartphone. The sensor is used for the detection of vital physiological parameters such as blood pressure, heart rate, respiration rate, blood oxygen, and body temperature.
Rapid response and remote care form the key foundation of smartphone-based monitoring technology. The cost and accuracy of the technology will be reduced as more and more companies enter into this domain, along with people embracing it with enthusiasm.
Collaboration between competitors and technology companies would bring some of the fantastic products addressing unmet needs such as non-invasive diagnostics.
References
Share your focus area or question to engage with our Analysts through the Business Objectives service.
Submit My Business ObjectiveOur long-standing clients include some of the worlds leading brands and forward-thinking corporations.




























