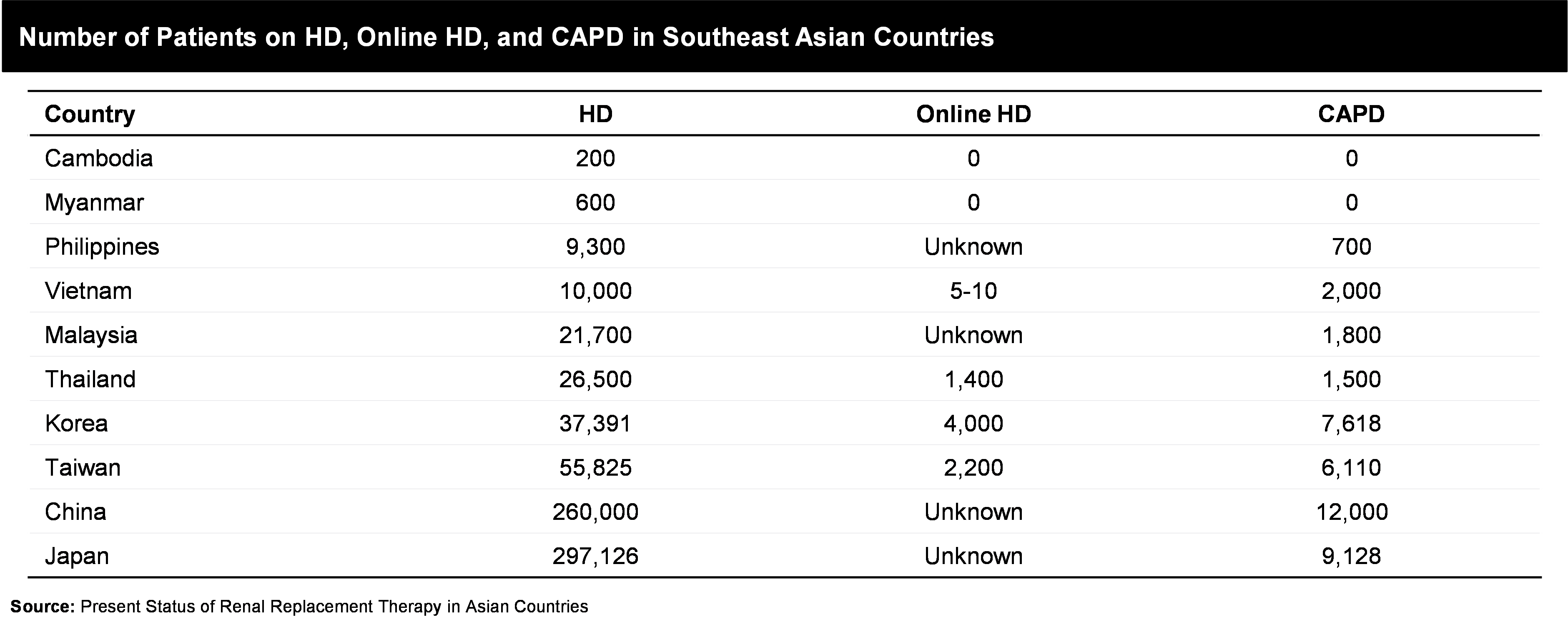
Another interesting factor is the amount of health care spending, and it has also been observed that provider and insurer models also impact the treatment rates. Use of private providers can enhance the associated costs, therefore publicly provided system as that in Hong Kong, can be affordable for patients and can lead to higher treatment rates. The stats depicts that though different countries have varied dynamics, but the market still has potential for more growth which can be tapped through at-home renal care services & offerings.
The reimbursement structure is another facet of how the current market dynamics of renal care segment is getting impacted. Currently, the specific strategies to decrease the financial burden of ESKD, such as programs to stimulate prevention of progression of CKD or promote the most cost-saving dialysis modalities are underutilized. To manage the cost effectiveness of the dialysis related treatment, the government are planning & adopting different payment models and system. The objective of the government is to offer quality care along with medications at controlled costs, that can be little overwhelming for dialysis providers. Bundled payment are getting adopted highly across different countries because it has encouraged dialysis provider to focus on how they can achieve the best patient outcomes while restraining costs.
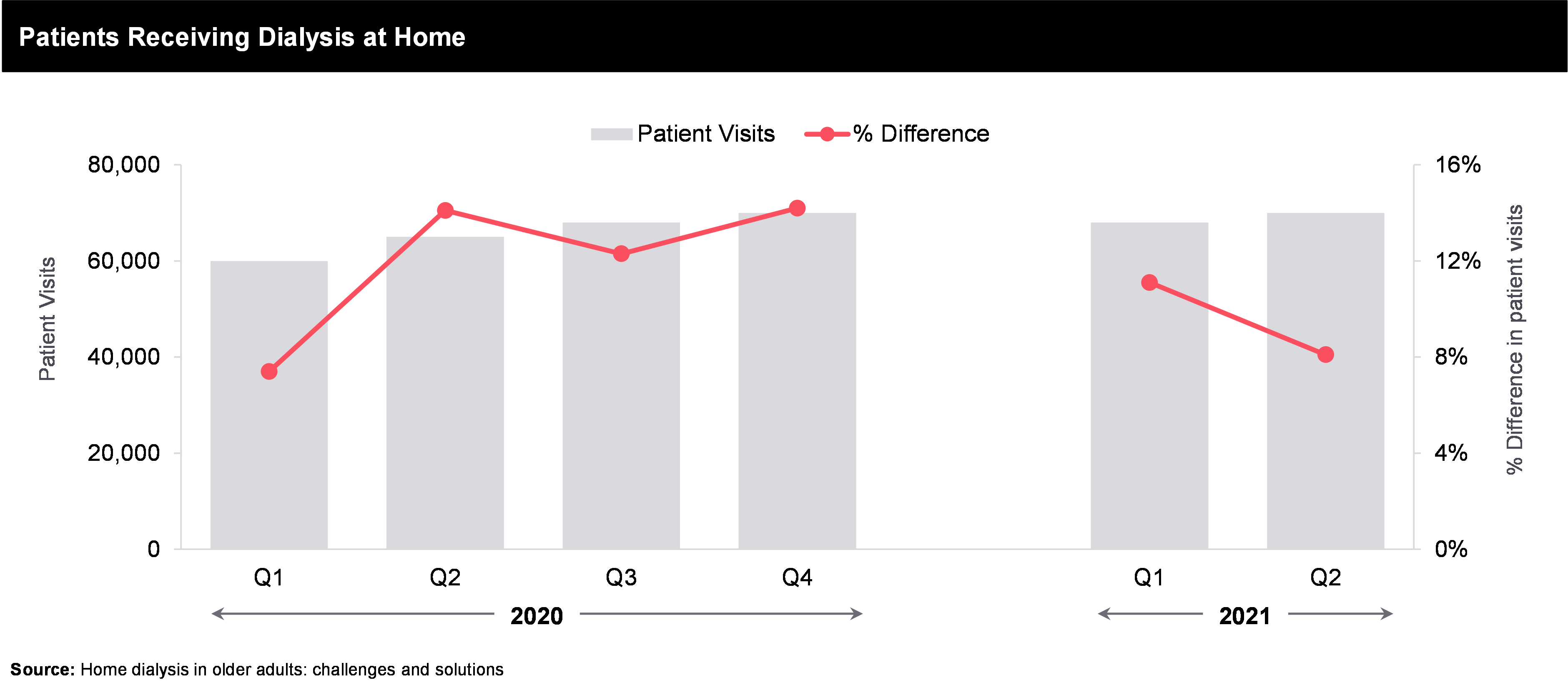
Bundled payments cover everything needed for outpatient dialysis, including medications (except pills until 2025), supplies, and other services previously billed separately. The government agency in charge of dialysis payments (CMS) expected to pay around $9 billion to 6,000 clinics in 2017 for these bundled costs. Since bundling, there’s been a shift in treating other complications like hyperparathyroidism with medications. New drugs have also been approved for managing end-stage kidney disease. Additionally, there’s been a small increase in patients using home dialysis, especially peritoneal dialysis (PD), instead of in-clinic hemodialysis (HD). Studies suggest home dialysis could be better for many more patients than currently use it. Doctors are taking note of this data and trying to improve patient outcomes and quality of life on dialysis, which often means encouraging home dialysis use.
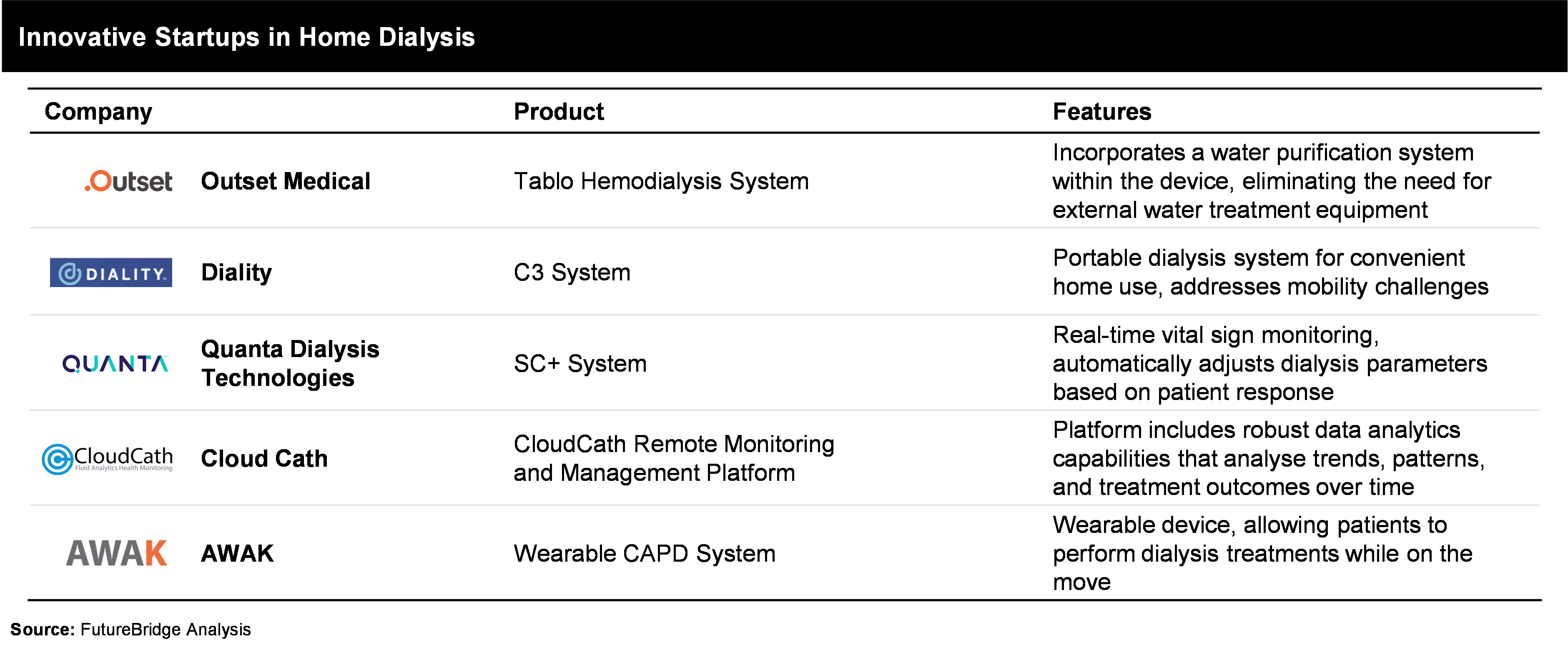
With evolving ecosystem, innovation solutions can increase the adoption of for example, establishing community houses for home hemodialysis (HD) can be one such way. Additionally key players are also focusing on developing better and smart home dialysis machines, due to multiple benefits like, cost efficient, greater convenience, flexibility, and quality of life.