Diabetic patients require daily blood glucose checks and insulin injections to maintain their blood glucose levels within the target range. Technology improvements have caused a substantial change in diabetes management in recent years.
Referring to diabetes cure technology, the doctor probably means technology that makes it easier for diabetic patients to take insulin or technology that measures their blood sugar levels. This technology for managing diabetes comes in many different forms, including insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). CGM has taken the place of finger pricks, while insulin pumps have simplified the administration of insulin.
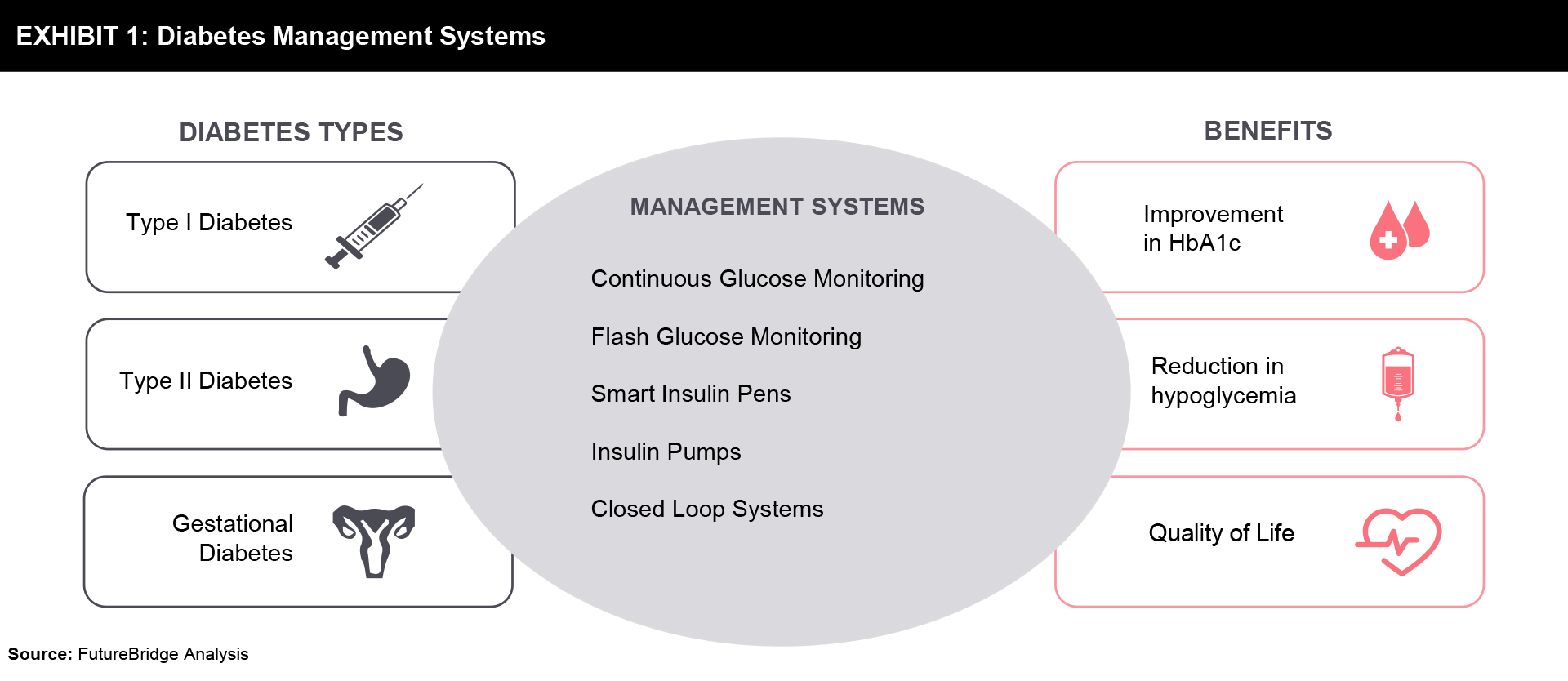
An advance directive for the treatment of diabetes should be adopted. Absolute insulin insufficiency results from type 1 diabetes, which is caused by autoimmune pancreatic beta-cell death. The treatment of type 1 diabetes has recently benefited from significant technical advancements. New insulin administration devices and interstitial glucose-based glucose testing devices are two examples of these. The quality of life and glucose management in this condition may be enhanced by these technologies. Type 2 diabetes, which is on the rise and accounts for 90% of all instances of diabetes worldwide, is a serious health concern. Insulin therapy is often necessary as the condition worsens due to the resulting insulin shortage and hyperglycemia. Although it is obvious that many type 2 diabetes patients need their treatment to be intensified, this does not always happen. This may be because of individual preference, limited health literacy, or fear of side effects. An increased risk of diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes mellitus in females, is associated with gestational diabetes mellitus. Prenatal diagnoses of gestational diabetes mellitus are becoming more frequent and have a significant impact on mother and fetal morbidity. Recent technological developments offer useful ways to simplify glucose monitoring and increase the precision and safety of insulin administration. This has made diabetes detectable and controllable with comfort. There are many diabetes management systems as shown in Exhibit 1 which help diabetic patients achieve a better quality of life.

Technologies for Glucose Monitoring
Diabetes requires a high burden of care making it associated with poor quality of life. To improve the condition of diabetic patients, there are technologies available for glucose monitoring.
Self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG)
Self-monitored blood glucose with finger stick glucose (FSG) concentrations is the rapid care for diabetic care. It is a method by which people with diabetes measure their blood sugar using a blood glucose meter. Based on the readings, people can adjust or check the effectiveness of their treatment. It has raised the capacity to find blood sugar measurements and support therapy accordingly. It helps to control blood glucose levels and cure hypoglycemia.
The enhanced speed of SMBG may raise glycemic control. There are a few more advanced new glucometers with blue tooth enabled that can be operated with smartphone applications for better detection and patterns. There is a restricted use for FSG as they provide the current glucose information but cannot detect glucose trends or the change associated. In the broader context of diabetes self-management, self-monitoring promotes maintaining blood glucose levels as close to target levels as possible.
Continuous glucose monitoring devices (CGM)
In recent years, insulin-treated patients have been increasingly using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems as an alternative to self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) systems. The spot blood glucose measurements and the lack of information on trends or changes in blood glucose limit the clinical utility of SMBG devices and do not detect nocturnal or asymptomatic hypoglycemia. With the ability to overcome these limitations, instant blood glucose monitoring and continuous blood glucose monitoring (CGM) have become more popular. The data provided by CGM can help in finding insulin doses and the proceeded therapy selection. The handy CGM technology is convenient due to its automatic functioning and collection of data regarding glucose levels. Some of the features of CGM devices are:
- CGM devices check and measure especially interstitial glucose continuously with regular updates in set minutes.
- These CGMs are having a monitor for the display of readings or information with regular real-time data and alerts/alarms. The monitor can be on your mobile screen too.
- It also has a sensor that can be implemented into the respective tissues with the transmitter attached to transfer the sensor data to the monitor.
- CGM can detect impending hypoglycemia, and find a wider range of glucose level fluctuations.
Improvements in design and accuracy have accelerated the use of the CGM devices in people with type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. In addition to the glycemic benefits of CGM, the ability to review continuous blood glucose data has been recognized to promote healthy lifestyle habits and motivation to exercise, reduce insulin resistance, and improve health, and cardiovascular disease in this high-risk group.
Technologies for Insulin Administration
The technology association for the quick and accurate Insulin Administration can have:
Insulin pens/Smartpens
Smart pens are next-generation insulin delivery systems that combine a reusable injector pen with a built-in smartphone application to enable diabetics better control the timing and amount of insulin delivered to their bodies. Additionally, the quality of the insulin is estimated by these devices, along with its shelf life and storage circumstances. They also communicate pertinent information to the doctor as necessary. An insulin pen is a reusable device as one can purchase them as an accessory for their existing insulin pen or in reusable form with cartridges that have been prefilled. With the smart pen calculation and tracking of doses becomes easy with the on-time reminders, reports, and alerts. This is the most popular way for type 2 diabetic patients to administer insulin with these insulin pens.
Some features of the insulin pen:
- It finds the exact dose based on the latest blood sugar level and does the calculation of insulin dose as per the recent meal proportion, carbohydrate amount, active insulin, and the rest of the prescription from the doctor.
- It also provides exact half-unit doses as per the requirement.
- Reminders and alerts prevent missing doses. The alert for the expiry of insulin or if it crossed its temperature range makes diabetic patients change the cartridge.
- An automated system helps to match the dose needed for a meal to help balance high blood sugar levels.
- Proper communication with the healthcare team or with the doctor as per the need related to diabetic data.
- The ability of smart insulin pens to transfer CGM data along with the aforementioned capabilities to internet platforms, allowing medical practitioners to remotely examine and modify therapy, is perhaps the most helpful feature.
Insulin Pumps
An insulin pump complements diabetes control and reduces the threat of hypoglycemia. Insulin pumps are devices that deliver a series of putting insulin through the inserted cannula in the tissues as continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII). The insulin pumps are available with the infusion set having a tube to deliver insulin. However, there are some devices called patch pumps that directly get attached to with the skin without any tubing.
These pumps have well-set programmable bolus and basal but that can change as per the timings of the day. These pumps help to track insulin coverage for the meal with the bolus calculator. The calculator helps to maintain the correct level of glucose. The fluctuations of doses can be corrected with the tracking process and can be adjusted by the pump. It can use varied basal rates at different times of the day. It is a short-term basal rate basically to adjust the glucose trends. It helps to provide an extended duration of meal time bolus insulin. The process makes your insulin dose corrected as per the glucose trends.
Automated Insulin Delivery System (AID)
An automated insulin delivery system is an effective system that is safe and helpful in preventing glycemia situations in an individual who is suffering from type 1 diabetes. AID systems are also known as closed-loop, artificial pancreas, or bionic pancreas systems which are composed of a controller, an insulin delivery device such as an insulin pump, and a glucose sensing device such as a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). In this system, the real-time glucose measurements that are implemented into a control algorithm automatically adjust the rate of subcutaneous insulin delivery via an insulin pump. The clinical assessments and practices are advanced up to the level to have the AID system approved for children and adults. There is an area of concern related to the subpopulations like young children, pregnant women, etc. with the improvement of the AID system. The improvement of the AID system is still going on and taking the need of subpopulation as input for improvement.
Advancement in CGM Devices
For more than 40 years, the idea of implanted glucose sensors has been promoted. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is now widely acknowledged to improve quality of life by enabling informed diabetes management decisions as a result of more effective glucose control.
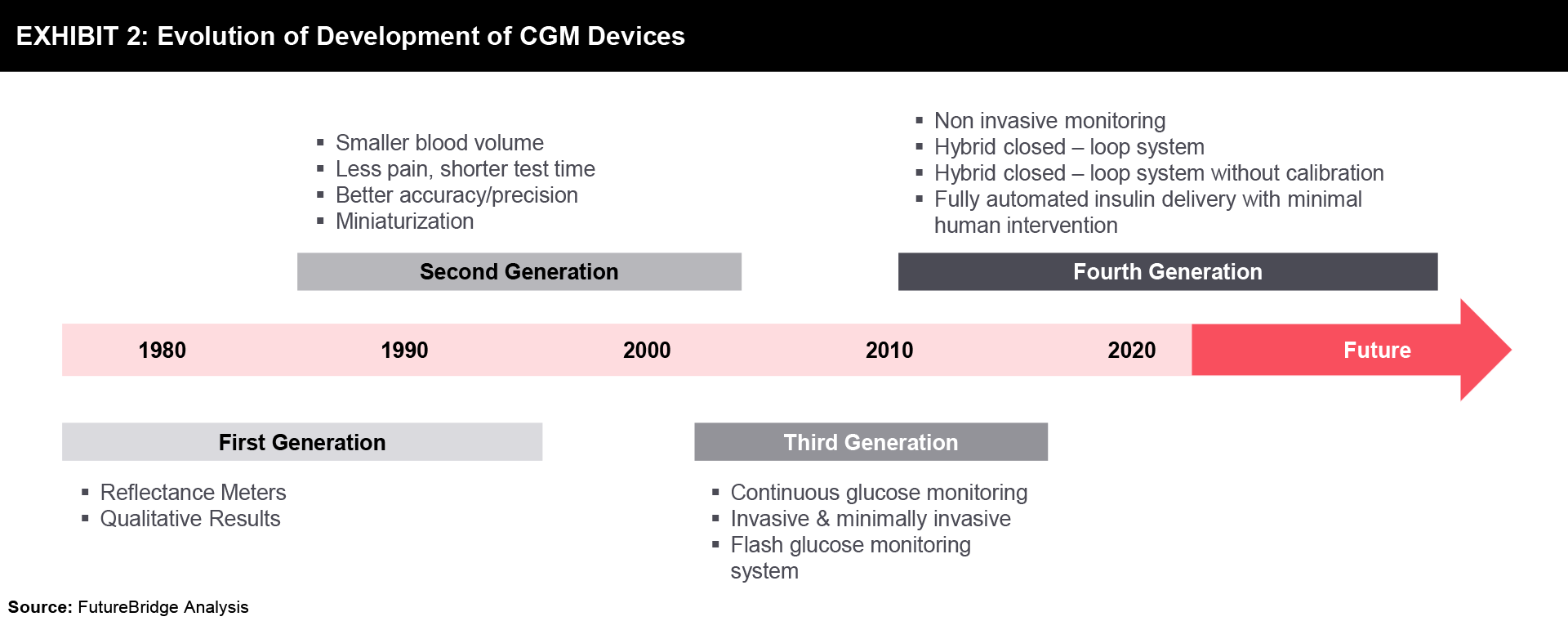
Evolution of CGM Devices
A brief timeline, representing the development of CGM devices over the last 40 years has been shown in Exhibit 2.
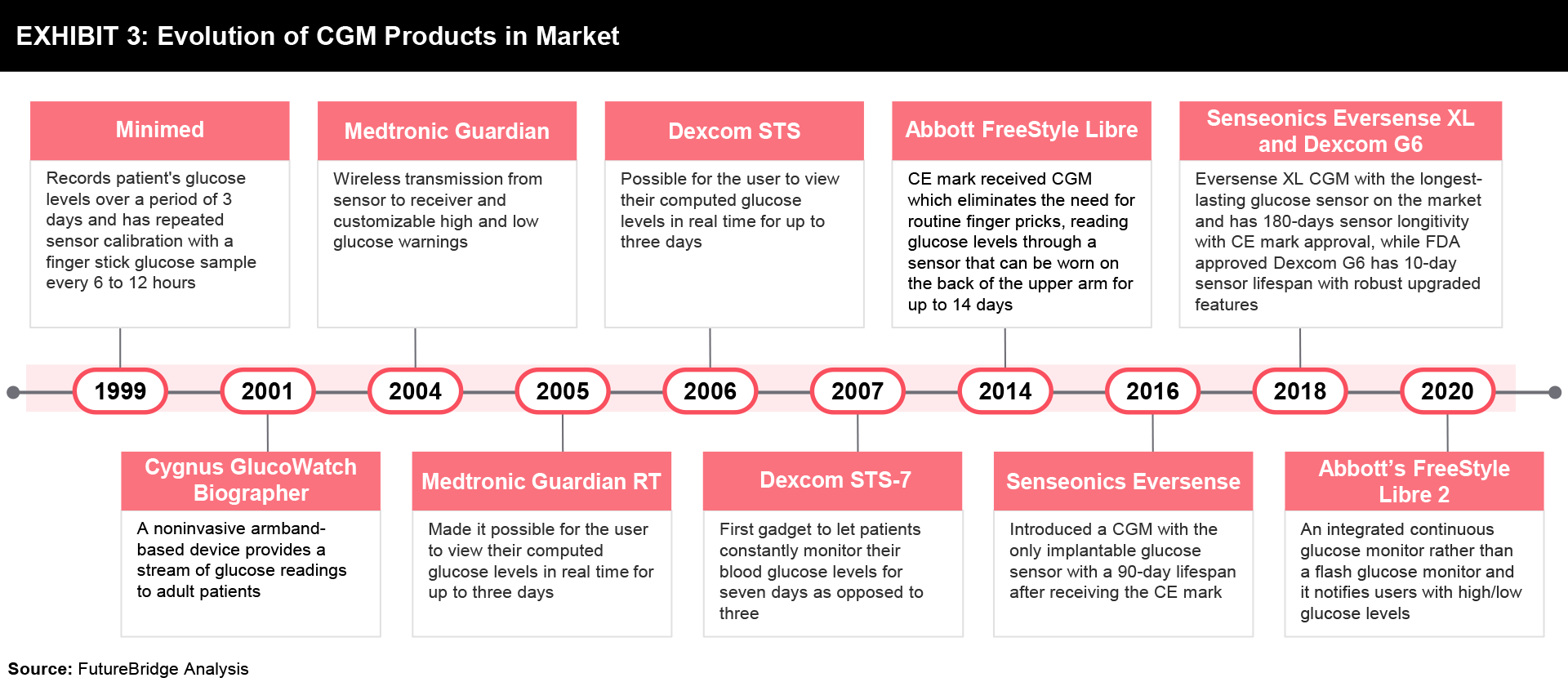
Further, the release of some CGM products in the market is outlined in Exhibit 3, while the details are mentioned below:
- The first CGM device, marketed by Minimed in 1999, allowed for the recording of a patient’s glucose levels for three days and required repeated sensor calibration with a finger stick glucose sample every 6 to 12 hours.
- In 2004, the Medtronic Guardian introduced features that later became industry standards such as wireless transmission from the sensor to the receiver and customizable high and low glucose warnings.
- The introduction of the Medtronic Guardian RT and the Dexcom STS, which were released in 2005 and 2006, respectively, made it possible for the user to view their computed glucose levels in real-time for up to three days.
- The STS-7 was the first gadget to let patients constantly monitor their blood glucose levels for seven days as opposed to three, and it was developed by Dexcom in 2007. Before the STS-7, Dexcom concentrated mostly on the development of a fully implantable glucose sensor device that could operate for a period ranging from one month to one year.
- Abbott received the CE mark for FreeStyle Libre in 2014. The FreeStyle Libre fully eliminates the requirement for initial and repeated finger-stick calibrations. The user could check their current glucose value and glucose level trends by scanning the receiver over the sensor with this device.
- The availability of auxiliary transmitters like Dexcom Share and MiniMed Connect in 2015 made mobile device compatibility a need for CGM devices. Although these devices allowed users to view their glucose results on their smartphones in conjunction with company-provided apps, it wasn’t until Dexcom produced the G5 that the requirement to carry a separate receiver was removed.
- Senseonics Eversense introduced a CGM in 2016 with the only implantable glucose sensor with a 90-day lifespan after receiving the CE mark. After one year, Senseonics introduced the Eversense XL in 2017, with a 180-day sensor longevity claim. The Eversense XL is still the CGM with the longest-lasting glucose sensor on the market.
- The FreeStyle Libre, the first flash glucose monitoring system with multiple game-changing improvements, was introduced by Abbott in the US in 2018.
- Abbott’s FreeStyle Libre 2, which was introduced in the U.S. in 2020, is an integrated continuous glucose monitor rather than a flash glucose monitor. It notifies users when glucose levels are high or low without requiring them to scan the device.


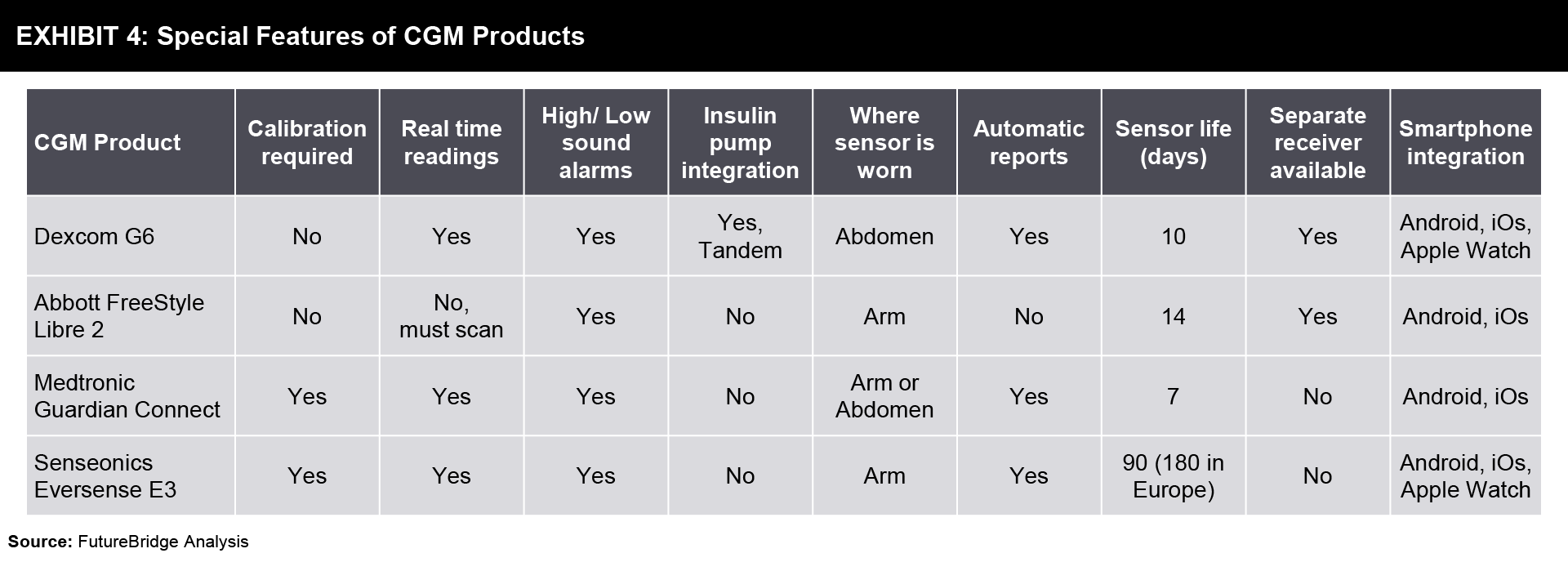
Special Features of CGM Products
There are a lot of companies providing CGM systems that require a sensor to be placed under the skin. Some of the special features of CGM devices offered by a few companies are compared in Exhibit 4.

More in the future is Abbott’s Freestyle Libre 3 which will have real-time CGM enabling a person to check at any time and see their readings. In Europe, Medtronic’s Guardian 4 sensor used with the most advanced MiniMed™ 780G insulin pump system demonstrated improved user experience and strong glycemic outcomes. Dexcom G7 will have a fully disposable transmitter sensor combination.
Future of CGM Devices
Future innovations in continuous glucose monitoring devices are moving towards integrated devices where players are integrating their CGM devices with an insulin delivery mechanism that is programmed to automatically deliver insulin upon detection of low glucose levels. Players are increasingly partnering with insulin pump companies to provide integrated/automated/closed loop solutions to end users.
Microneedles are increasingly being used as part of minimally invasive continuous glucose monitoring systems to reduce pain and provide comfort. Microneedles are relatively painless and can be implanted more easily when compared to older implantable sensors. Functionalized microneedles are mainly used for two purposes in CGM systems: as a sensor probe/electrode and as biological fluid collection materials.
Many companies are exploring the development and improvement of CGM devices for the non-invasive monitoring of diabetes. Despite the market’s abundance of biosensing platforms for glucose monitoring, there is still a critical need to improve the accuracy, reproducibility, wearability, and accessibility of these systems for end users. More and more research is being done on biosensing technologies, which use various biological fluids like perspiration, tear fluid, etc., that may be calibrated and used to assess correct blood glucose concentrations. Also, the use of exponential technologies like virtual reality, augmented reality technologies, etc. for glucose detection apart from the integration of non-invasive sensors into various wearable formats for non-invasive/ pain-free detection methods is being explored. Other than sensors, there is research going on using fluorescent gels for continuous glucose monitoring where the fluorescent gels are implanted into the living body which exhibits fluorescence response by bonding with glucose.
Conclusion
As per the research data, the future trends will be very exciting with the scope of diabetes management approach having the patient as the focal point. The technological support of the field made the prevention better with the high-tech devices. One can take care of their diabetes with tracking devices. The automated devices can track glucose levels and help patients take action on time towards diabetes control. Further in many patients, CSII-assisted insulin delivery is a well-respected therapy that has shown particularly effective in lowering hypoglycemia and enhancing glucose control.
The expectations are booming with the entrance of nanotechnology in the future of diabetes cure. The technology will be capable to detect diabetes before the symptoms appear to anyone as per the prediction. The technology will measure glucose and induce insulin into the bloodstream directly. Still, all are on the cloud but the future of inventions and research output will be excellent and can be the cure for diabetes for millions.
References
- Leveraging advances in diabetes technologies in primary care
- New and emerging technologies in type 1 diabetes
- Continuous glucose monitoring
- Insulin delivery devices
- Smart insulin pen
- The future of diabetes management
- Automated insulin delivery system
- Continuous glucose monitoring-past, present, and future
Need a thought partner?
Share your focus area or question to engage with our Analysts through the Business Objectives service.
Submit My Business ObjectiveOur Clients
Our long-standing clients include some of the worlds leading brands and forward-thinking corporations.
- © 2021 Cheers Interactive (India) Private Limited. All rights reserved. FutureBridge ® is a registered trademark of Cheers Interactive (India) Private Limited.




































