Machine Vision: The Future of Quality Control in Manufacturing
What’s machine vision?
Machine vision is a form of robotics technology that uses digital images and cameras connected to a computer in order to acquire information. It works by taking readings from digital cameras or image acquisition hardware and applying them to algorithms. This allows machines to successfully identify and catalogue various objects in the environment. The hardware component of machine vision is composed of a digital camera, light sources, lenses, and possibly other components like reflectors and filters. These all work together to capture the image. The software for machine vision works by processing and categorizing the images acquired by the camera, making them ready for analysis.
Machine vision technology is now becoming increasingly popular in quality control processes, such as for detecting defects. It can also be used to measure the dimensions of objects or to compare objects with a sample. This technology not only increases efficiency and accuracy but also reduces the need for human involvement, increasing safety. It can be used in a wide range of industries including the automotive industry, aerospace, and medical manufacturing.


Importance of Quality Control in Industrial Manufacturing
Quality control (QC) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing industry that encompasses all activities and processes implemented to ensure products meet the required standards. It involves systematic and rigorous examination of raw materials, components, and final products. By meticulously monitoring every step of the production process, quality control ensures that the goods are consistent in their performance, reliability, and safety.
One cannot emphasize enough the importance of quality control in the manufacturing industry because it directly impacts the product performance, maintenance costs, customer satisfaction, and brand reputation to influence the business success. Businesses with high quality controls enjoy minimizing waste, reduced rework, product reliability and thus gain a competitive edge in their markets ultimately fostering long-term customer loyalty and trust.
Key Stages of Quality Controls in Industrial Manufacturing
The industry or the product heavily influences the Quality Control techniques utilized in a company. To ensure that the proper product reaches its customer, testing is done in accordance with standards specific to each business. Testing at various stages of production helps to spot production process faults and the corrective actions needed to stop them from happening again.
Every stage of the production process includes a variety of quality tests, and these quality controls may be fully or partially performed depending on the nation, sector, client, and product:
- Pre-production sample: The first stage of testing involves inspecting and evaluating the incoming raw material /components. This is crucial because defects and inconsistencies in the raw material/ components can negatively impact the quality of final product.
- Raw Material Inspection/ Technical Inspection: A second stage testing is done in laboratories. The raw material or the product is picked to conduct more thorough/ deeper quality analysis. The results of this analysis can be shared with the concerned parties as well.
- In-Line Inspection: During the manufacturing process, quality control and checks are performed, and these are often referred as In-line inspection. It involves inspecting the product at various levels of assembly line to identify and rectify the issues before they escalate. It saves time, money, and resources of the company and helps the company to take necessary precautionary measures for future products. Evaluating the product at regular intervals during the manufacturing process helps to pin-point the fault. It reduces the wastage, alteration, and remanufacturing of the entire product.
- Out-Line Inspection: The inspection happens as soon as the product leaves any production line. Like the In-Line Inspection process, this method offers more flexibility in finding errors and in implementing corrective plans.
- Final Inspection: This is the last opportunity for quality inspectors/ auditors to prevent shipment of a faulty product ad address the quality issues on time to prevent production of such product in future. This inspection is usually done when 100% of the order is manufactured and around 80% is packed. This test allows the auditor to decide whether to give the green signal for shipment of these products.
- Loading Inspection: Since a major part of industrial goods are labelled and packed before shipping to customer. A last step inspection is also done while labelling, packaging, and loading. This last step ensures that the goods are responsibly managed and safely loaded for a secured transportation.
Limitations of Traditional Manual Inspection Methods
The traditional processes used in quality rely on inspection by human operators and are prone to errors. On top of that there are other limitations of these processes such as:
- High Costs: Manual quality control processes require a lot of labour resources, which can raise production costs dramatically.
- Time Consuming: Manual quality control processes take a long time and require highly skilled personnel to make sure the products are up to standards. This can lead to delays in production and scheduling.
- Error Prone: Although manual quality control processes are done by highly trained personnel, human error is always a risk. Even the most experienced personnel can make mistakes, leading to defective products.
- Limited Coverage: A manual quality control process can only cover a limited area, making it difficult to check everything.
- Lack of Flexibility: Manual quality control processes are not very flexible and cannot easily adapt to different types of products.
Machine Vision for Quality Control: Key Benefits
Traditionally, quality control in manufacturing has relied on manual inspections by human operators, which can be time-consuming, subjective, and prone to errors. Fueled by the need of high-quality products with declining profit margins and stringent human safety regulations, the quality control processes have gone through automation and the quality control domain has experiencing a transformative evolution. While the past quality control systems relied heavily on manual intervention, the new and futuristic systems are employing Artificial Intelligence enabled by machine vision to detect even slightest imperfections. These new developments are revolutionizing the production lines and disrupting the entire manufacturing sector.
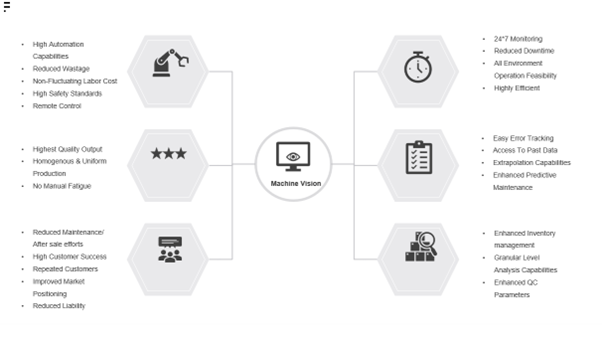
Machine vision offers several advantages over traditional quality control practices.
- Firstly, it improves inspection accuracy by eliminating human error. Cameras and algorithms can detect defects and anomalies with greater precision than the human eye. This ensures that only products meeting the specified quality standards are approved.
- Secondly, machine vision improves inspection efficiency by automating the process. Manual inspections can be time-consuming, especially for complex or repetitive tasks. Machine vision systems can operate continuously and at high speeds, significantly reducing inspection time and increasing overall productivity.
- Thirdly, machine vision enables real-time data collection and analysis. By capturing and analyzing inspection data, manufacturers can identify quality trends, monitor production processes, and make informed decisions to optimize manufacturing operations.
- Additionally, machine vision offers enhanced flexibility and scalability. The systems can be easily programmed to accommodate different inspection requirements and adapt to changing production needs. This flexibility allows manufacturers to easily integrate machine vision into their existing quality control processes without significant disruptions.
Benefits of Machine Vision Assisted Quality Control in Industrial manufacturing
Growth Opportunities for Machine Vision Based Quality Control Processes
The market for machine vision-based quality control processes is growing rapidly, driven by various factors. Firstly, the increasing complexity and diversity of products being manufactured require more advanced inspection techniques. Machine vision systems can easily adapt to different product types and perform inspections with high precision, making them ideal for industries such as automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage.
Secondly, there is a growing demand for improved product quality and safety. Defective products can lead to recalls, customer dissatisfaction, and even safety hazards. Machine vision helps manufacturers identify and eliminate defects early in the production process, ensuring high-quality and safe products reach the market.
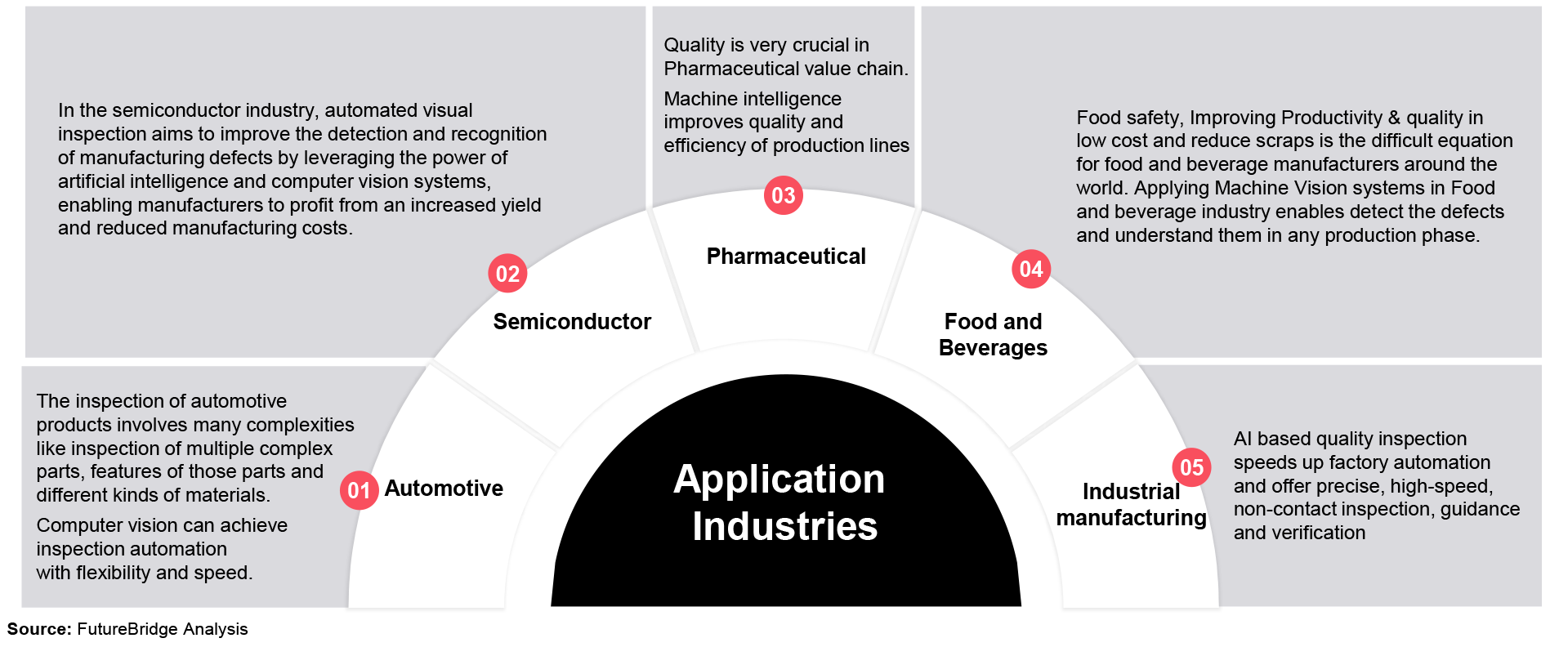
Some industries that are seeing growth in machine-vision based quality control:
- Automotive: Automakers are increasingly adopting machine vision-based systems in manufacturing for quality control, from inspecting car parts to ensuring cleanliness. This technology is used to ensure that parts are assembled correctly and that they meet engineering specs.
- Food and Beverage: Food and beverage producers often use machine vision-based systems for quality control, such as grading fruits and vegetables for sweetness or inspecting packaging for errors.
- Medical: Medical device companies are using machine vision-based systems for inspection and quality control. This technology can detect defects in surgical instruments and other medical devices.
- Pharmaceutical: Pharmaceutical firms use machine vision systems for tableting, capsule filling, drug sorting, and compliance checking; this technology will help ensure medication safety and accuracy.
- Power Generation: Machine vision-based systems are used in the power generation industry to inspect and maintain power turbines and related components.
- Oil and Petroleum: Oil and gas companies are using machine vision to inspect leads and pipelines for damage. These systems are also used to monitor safety processes in refineries.
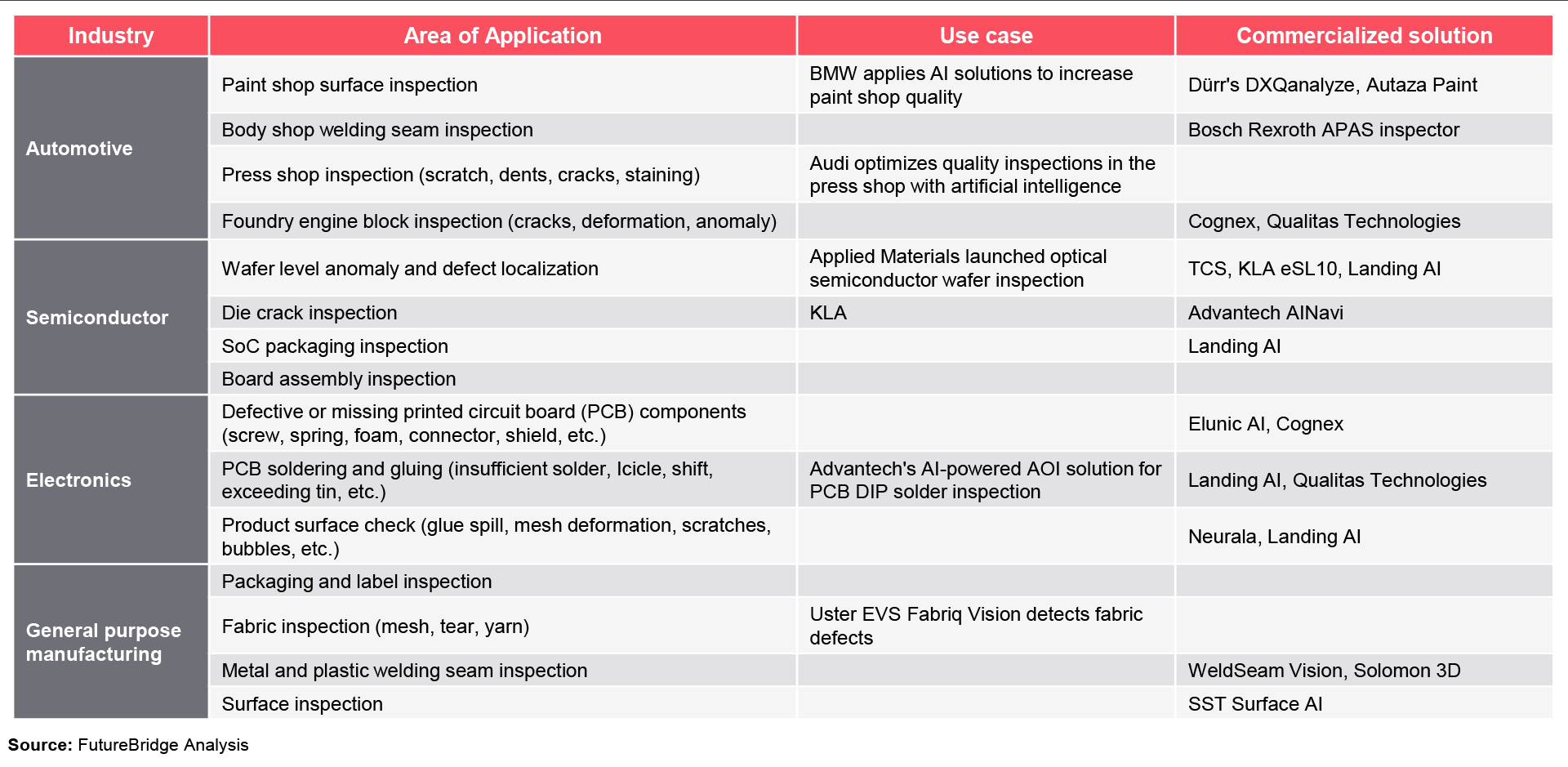
Several companies are actively utilizing machine vision in their quality control processes. In the automotive industry, machine vision is widely used for inspecting various components, such as engines, body panels, and electronic systems. Companies like Cognex Corporation, Keyence Corporation, and Omron Corporation provide machine vision systems and solutions specifically tailored for automotive quality control.
Other industries that heavily rely on machine vision-based quality control include electronics manufacturing, where components and circuit boards are inspected for defects, and pharmaceuticals, where packaging and labelling are examined for accuracy and compliance.
FutureBridge analysis indicates that majority of quality control research is focused on AI backed by machine vision systems. We anticipate more commercialization/adoption of these advanced quality control methodologies in coming future. It would also take leverage from the evolving deep learning technological advancements.
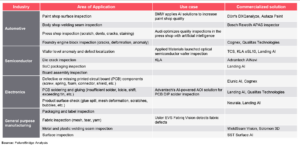
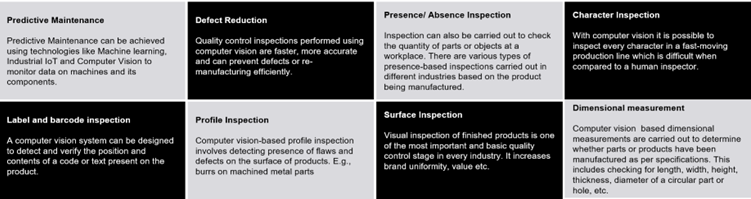
Machine vision-based Quality control – Use Cases/ Applications

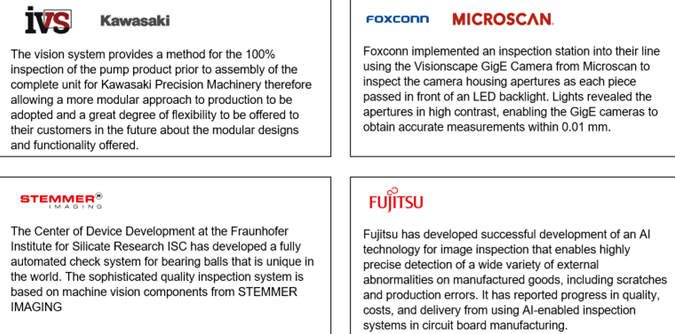
Key Industry Developments
The machine vision-based quality control market is witnessing a surge in startup activity and technological advancements. Startups such as Inspekto, VITRONIC, and Kneron are developing innovative machine vision solutions offering easy integration, affordability, and improved accuracy.
Market research reports also predict significant growth in the machine vision market for quality control processes. Factors such as the increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 concepts, advancements in AI and deep learning algorithms, and the need for improved quality control are driving this growth.



Conclusion
Machine vision is revolutionizing quality control processes in industrial manufacturing. Its accuracy, efficiency, real-time data analysis capabilities, and flexibility make it an ideal solution for industries looking to enhance their product quality and meet regulatory requirements. With market opportunities expanding and advancements in technology, machine vision-based quality control processes are poised for significant growth in the coming years. Furthermore, regulatory requirements and quality standards are becoming more stringent across industries. Machine vision offers a reliable and consistent method to meet these requirements and maintain compliance, reducing the risk of penalties and reputational damage.
To gain deep insights and create new milestones for your brand connect with FutureBridge consultants today.
Resources
- https://www.graphicproducts.com/articles/quality-control-in-manufacturing/
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/q/quality-control.asp#toc-what-is-quality-control
- https://www.sourceofasia.com/roles-of-quality-control-in-manufacturing-and-production-management/
- https://www.ibm.com/in-en/topics/computer-vision
- https://softengi.com/blog/computer-vision-for-quality-control/
- https://blog.vsoftconsulting.com/blog/top-usecases-of-computer-vision-in-manufacturing
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/08982112.2021.2001828
- The Leader in Industrial Machine Vision (cognex.com)
- Machine Vision in the Automotive Industry | AIA Industry Insights (automate.org)






































