Safety Challenges–Energy Storage Technologies
 Energy
Energy
Introduction
As the penetration of renewable energy into the grid is increasing day by day, the necessity of incorporating energy storage in the power systems is increasing. Energy storage can act as a standby power supply, can be deployed to compensate for the intermittency of renewable power generation, can provide ancillary grid services, and has the potential to differ transmission and distribution infrastructure investments. Countries across the world are aggressively focusing on the deployment of energy storage systems, be it grid-scale or behind-the-meter.
Despite all the services offered by energy storage systems, there is a barrier of safety issues around it. The explosion in an Arizona battery plant last year and fire incidence in South Korean plants in 2017 have highlighted the importance of safety in energy storage systems. The safety applies to product design, installation, service, decommissioning, and various steps in the supply chain.
Key Safety Challenges
There are different types of technologies that are being deployed for energy storage purposes. Battery technology dominates the market and finds its application from small scale home storage and electric vehicles to large grid-scale energy storage systems. Though it’s the most popular and widely deployed storage technology, certain safety issues are associated with battery technology. Some of the key challenges associated with battery storage are listed below.
- High voltage risk: Larger number of battery cells per string in grid-scale energy storage results in higher voltage levels and creates a risk for unqualified workers.
- Arc-flash/ blast: High string voltage affects the shock and arc-flash/ blast potential. This increases the risk of injuries.
- Fire: This is the most common issue observed in lithium-ion batteries. Fire is caused by thermal runaway which is a chemical process where self-heating in a battery exceeds the rate of cooling. This causes high internal temperatures, melting, off-gassing/ venting. In some incidences, thermal runaway can lead to fire or explosion. Combustion can also take place as a result of Hydrogen build-up from the charging of aqueous batteries.
- Toxicity: Electrolyte used in some flow-batteries can be toxic to the environment or human beings. Also, incidentally generated smoke from batteries can be toxic.
Developments around Energy Storage Systems Safety
Energy storage is emerging as an important component of a resilient and efficient grid. The evolving energy markets and clean energy transition will facilitate the increased need for energy storage. Hence, it is essential to address all the safety-related issues around energy storage.
Although penetration of energy storage is increasing worldwide, the U.S. seems to lead the industry. U.S. Department of Energy published the Energy Storage Safety Strategic Plan in December 2014 to discuss various safety aspects of energy storage. After the Arizona battery explosion, safety became top of the agenda in all project discussions. The country has taken energy storage safety very seriously and is working upon it. In December 2019, the Energy Storage Association issued U.S. Energy Storage Operational Safety Guidelines. Sandia National Laboratories and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory also published multiple documents relevant to safety in advanced energy storage under the purview of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Electricity Delivery and Energy Reliability Energy Storage Program. The organizations also conducted various workshops.
In September 2019, National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) released NFPA 855, a standard to inform designers, builders, facility managers, manufacturers, responders, and others about potential fire hazards. This is the first comprehensive collection of criteria for the fire protection of ESS installations which includes requirements based on the technology used in ESS, the size and separation of ESS installations, the setting where the technology is being installed, and the fire suppression and control systems that are in place.
Safe Alternative Battery Technologies
Though Li-ion batteries have captured the market, safety issues associated with these batteries have created the need for alternative technologies. A lot of efforts are being put in to find a technology that overcomes the limitations of Li-ion battery and is yet cost-competitive. Many companies have entered the market with alternative battery chemistries. Some of such technologies are listed in the following Exhibit 1.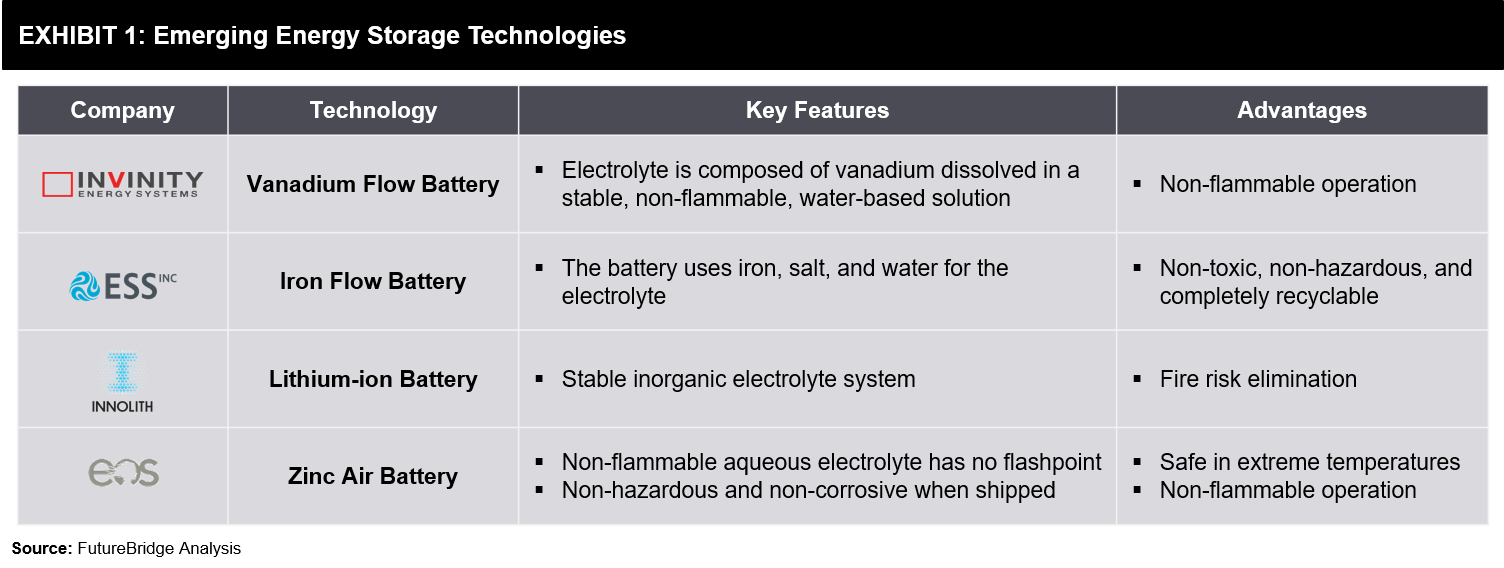
Industry Impact
The safety of energy storage systems is under scrutiny after the Arizona battery plant explosion in April 2019. The energy storage market is set to grow exponentially but the recent fire incidences may be problematic, especially for the lithium-ion battery industry. Safety issues related to energy storage technologies have resulted in several industry impacts some of the key impacts are described in Exhibit 2.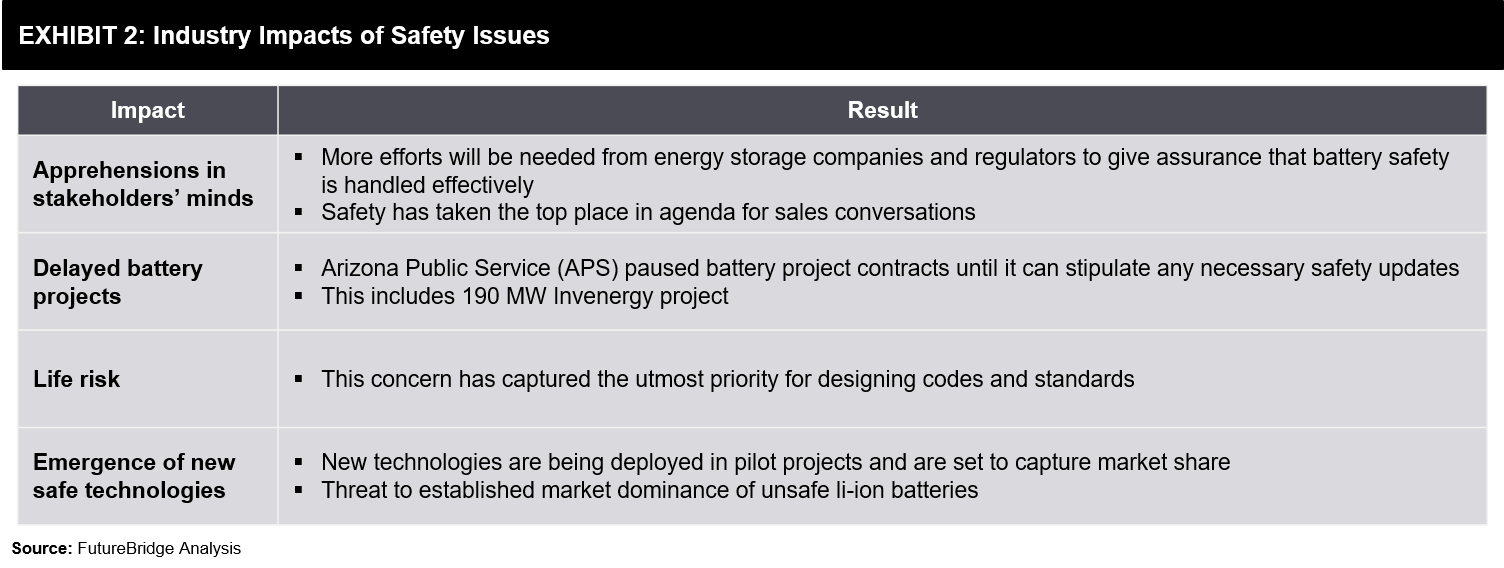
Future Outlook
Safety has always been a concern around batteries. The risk of thermal runaway is well-known for li-ion batteries. Energy storage is still relatively early in its technological maturation and it is unrealistic to expect no such fire incidences in the future. It is important in this context to learn lessons from the failure events and try to build safer systems. Rolling out safety guidelines, standards, correct controls, and measures will help the industry to grow with confidence. Safety advice and precautions from the energy storage companies and training workshops on the same can help reduce the risk. Change in conventional battery safety engineering to meet the standards is also needed.
The development of emerging safe technologies can be considered for a wide range of storage applications rather than focusing only on measures to avoid hindrance for the growth of matured unsafe battery technologies. The future growth of the energy storage industry depends upon how market players move decisively to build confidence in the safety of energy storage technologies.



 5 min read
5 min read
































