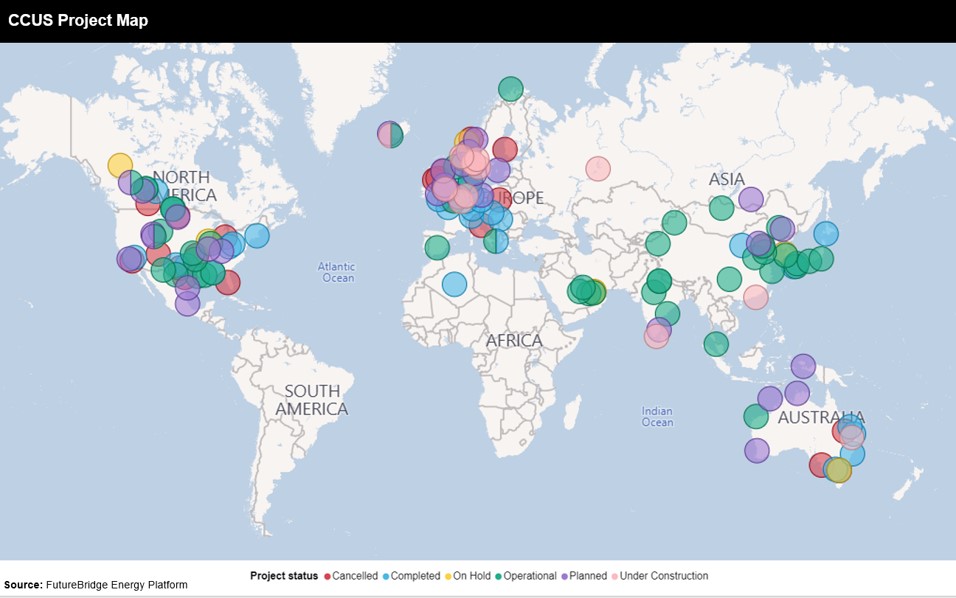
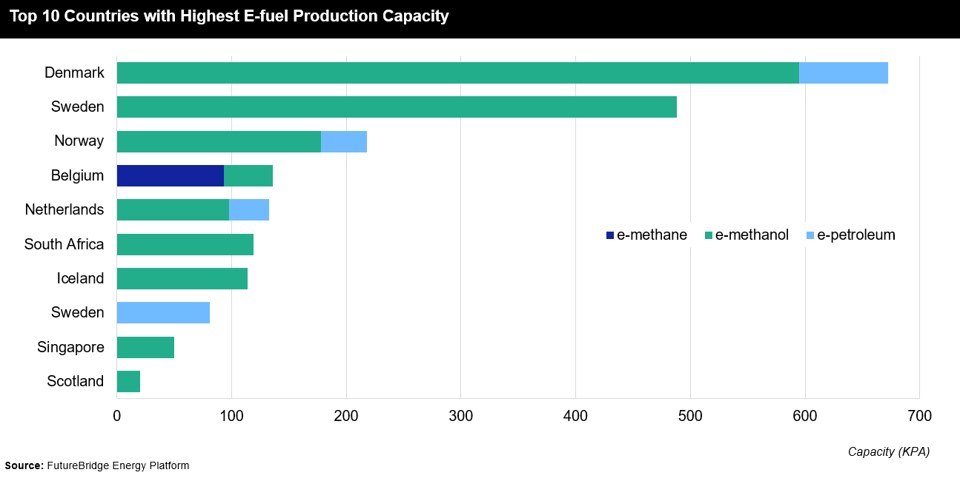
The key challenge in CCUS deployment is scalability. Promising pilot projects exist, but transitioning to large-scale deployment necessitates significant infrastructural and logistical considerations. Ensuring the scalability of CCUS technologies requires coordinated efforts from governments, industries, and technology providers.
The economic viability of CCUS is crucial for success. Initial costs in technology development, infrastructure setup, and operational maintenance create barriers. Collaborative efforts between technology providers and industries drive down costs through shared expertise, innovations, and economies of scale.
Unlocking the full potential of CCUS requires the right funding mechanisms. Pioneering companies and industry developers must tap into accessible funding channels. The recent commitment of $15 billion from ADNOC for energy transition is a significant stride, yet a broader collaboration is essential to mobilize the financial resources required for large-scale deployment.
- Legal Frameworks and Legislation:
Legal frameworks play a pivotal role in creating an environment conducive to CCUS deployment. Legislation that incentivizes carbon capture and utilization, coupled with penalties for excessive emissions, can drive businesses and customers toward cleaner practices. Standardizing legal platforms also ensures a consistent and predictable landscape, fostering confidence among stakeholders.
- Stable and Predictable Policies:
CCUS deployment necessitates stable and predictable policies. Economic valuation becomes more straightforward when industries have a clear understanding of government regulations, subsidies, and incentives. The creation of standardized metrics for cleaner energy production can guide businesses in aligning their strategies with environmental goals.
- Business Decision Dynamics:
Understanding the business motivations behind CCUS adoption is crucial. Beyond environmental considerations, businesses weigh the economic implications, considering factors such as the carbon pricing mechanism. A transparent and standardized evaluation process for carbon capture and storage encourages businesses to align their decisions with sustainability goals.
The roadmap ahead involves transcending barriers, leveraging innovative technologies, and fostering a global commitment to sustainability. By addressing these strategically, we can pave the way for a future where CCUS becomes a cornerstone in the global transition to a low-carbon economy. It’s not just a technological endeavor; it’s a collaborative journey toward a sustainable and resilient future.
Crucial Role of Technological Innovation in Addressing Climate Challenges
This insight emphasizes the pivotal role of technological advancements across sectors, highlighting the interconnectedness of innovations to create a comprehensive and effective approach. The discussions surrounding Direct Air Capture (DAC), biofuels, ammonia, and blending technologies underscore the critical role innovation plays in the global fight against climate change.
DAC, a groundbreaking innovation, shows promise for reducing the aviation sector’s carbon footprint by directly extracting carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This not only curtails emissions but also offers a path to carbon neutrality. Mainstream adoption requires collaboration among technology developers, governments, and aviation stakeholders. Legislative support and a clear demand for sustainable aviation fuels will be pivotal in driving DAC technology adoption.
- Ammonia and Methanol as Future Fuels:
The future of sustainable fuels revolves around ammonia and methanol, with an annual production capacity of 80 million tonnes. These chemicals have the potential to replace conventional fuels, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. However, their widespread adoption requires a concentrated effort to develop blending technologies. The insights emphasize the necessity of governmental legislative support to create demand for cleaner fuels. Blending cleaner alternatives with conventional products is seen as an ideal transitional approach and facilitating a smoother shift toward sustainable energy sources.
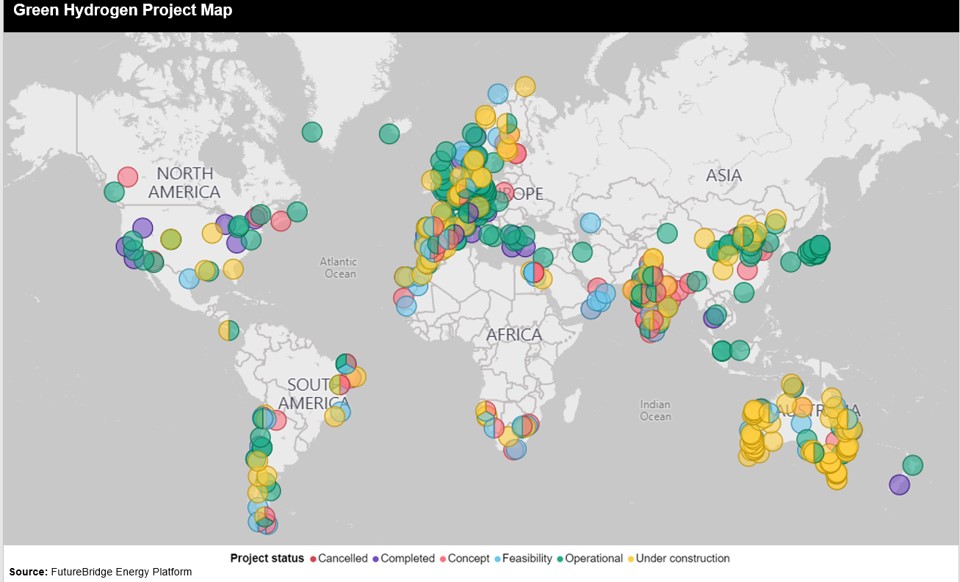
Utilizing renewable feedstocks, like animal fats, demonstrates higher efficiency and a reduced environmental footprint. The insights highlight the transformative potential of e-fuels (electro fuels) as the cornerstone of clean energy. Green hydrogen (H2) and carbon utilization from captured carbon further bolster the development of a circular economy. Thriving on these innovations requires imperative collaboration among industries, researchers, and policymakers. The following Exhibit 3 shows the global green hydrogen map.