Globally, the most common insulating materials, such as concrete, mineral wool, fiberglass, and various foams, have a significant environmental impact due to high-energy manufacturing processes and reliance on petroleum or natural sources. This underscores the need for sustainable alternatives in building insulation. Researchers are exploring the thermal and acoustic insulating properties of bio-waste materials, industrial by-products, and recycled alternatives to develop greener solutions, promoting sustainability in the building insulation industry.
Exhibit 1 shows different sustainable/ circular insulating material alternatives.
A variety of raw materials including Bagasse, Corn cob, Cotton stalks, Straw bale waste, etc. can be used for insulation. In some cases, Recycled glass, Recycled Denim or cotton, recycled PET, and textile fibre are used as well.
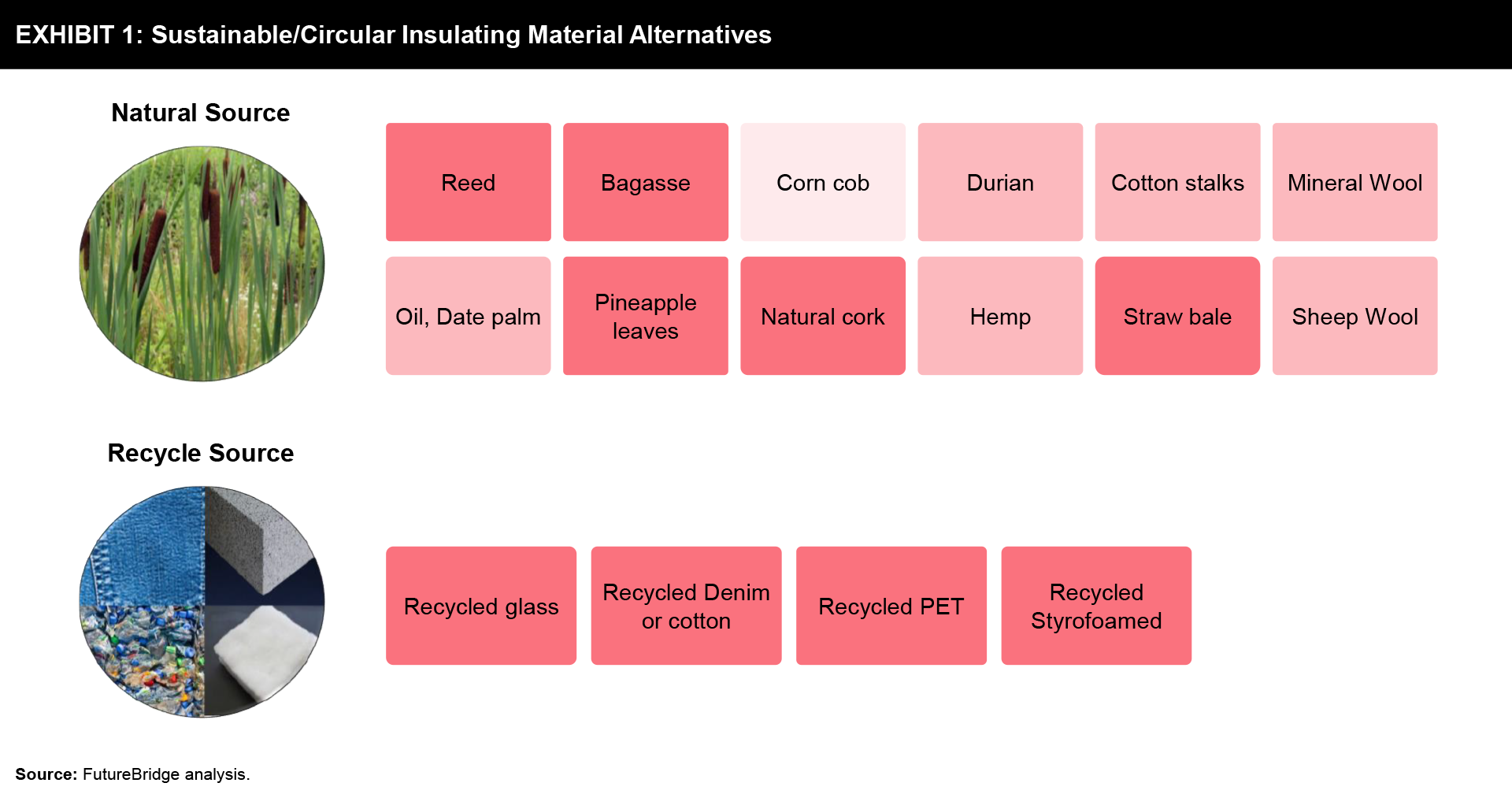

Recycled petroleum-based polymer or using industrial by-products to produce new materials can be a sustainable strategy to reduce the use of virgin material and its disposal in the landfill. Comparative analysis shows synthetic recycled materials have good thermal insulating properties compared to natural ones.
Innovative Insulation Material from Natural Origin or Recycled Origin
Newer alternatives like various waste biomass, agro residues, recycled plastics or polymer and other natural resources are being investigated to achieve sustainability. The unconventional material can reduce the use of oil-based and not renewable sources. While looking at different insulations, R-value is one of the features most often used to compare insulation efficiency. The sustainability performances of different insulating materials are calculated based on the carbon emission and energy consumption during the product life cycle. The material energy consumed in the extraction and manufacture of insulating materials should be low.
Exhibit 2 shows a comparison between different insulation materials based on their R-Value, health and safety concerns, overall sustainability as well as durability of the products.
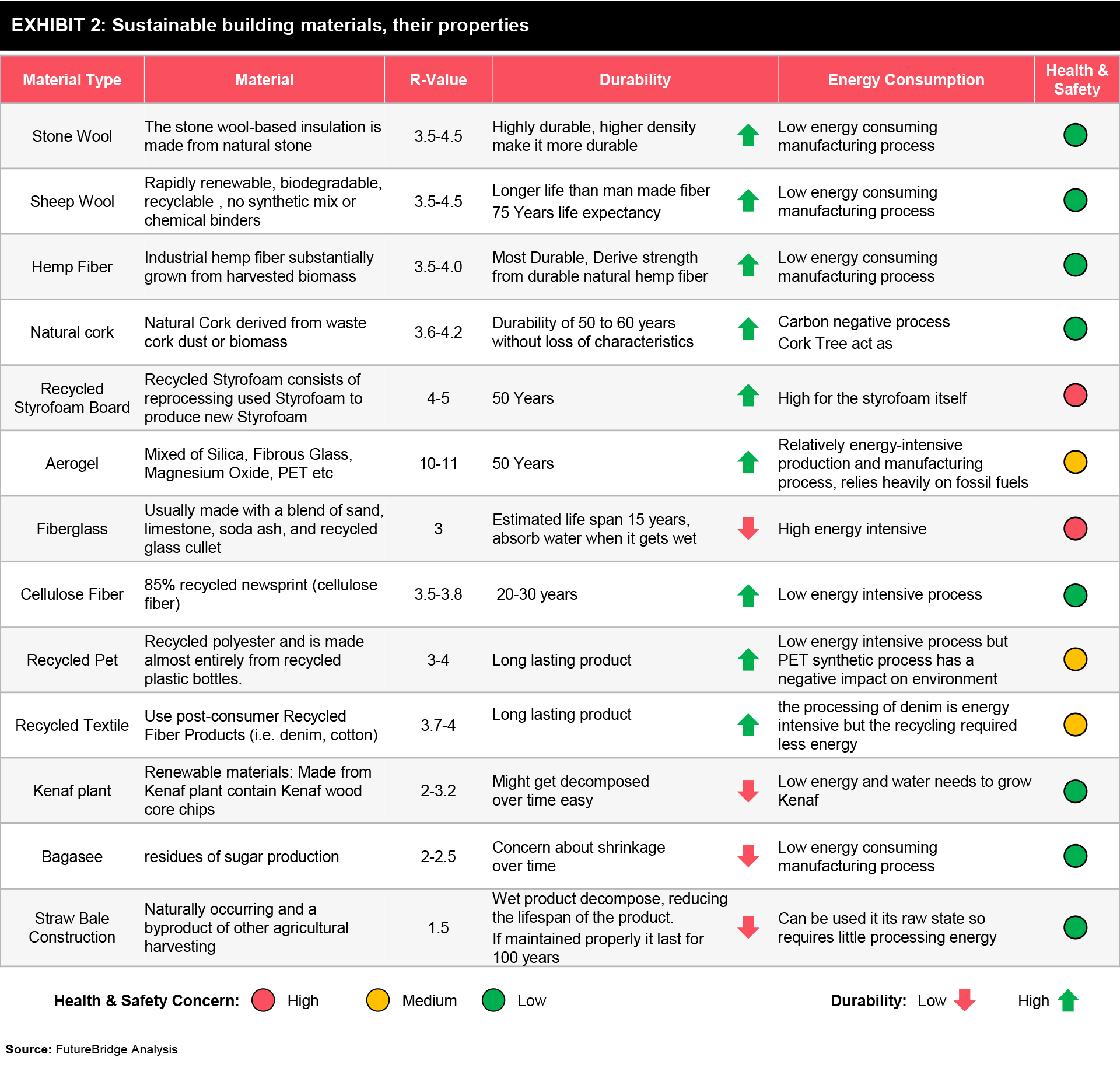

- Considering all the perspectives together natural stone wool-based insulation material excels in almost every category and can be considered a sustainable materials.
- Sheep’s wool can keep the home warm the same way it helps sheep survive frigid temperatures. In recent years, scientists have figured out how to apply the insulating properties of sheep’s wool to home construction.
- Hemp Fiber based insulation is a highly sustainable material that required little energy, sequesters carbon, and is naturally pest-resistant but the product might have a negative impact on moisture resistance.
- Another natural insulating material is the natural cork which is made entirely of cork and water, without any additives or adhesives. The product is highly moisture management, has low water absorption and is highly durable. The major disadvantage is the high cost per sq. ft per R-rating.
- Straw Bales are made up of 100% straw a naturally occurring byproduct of another agricultural harvesting. It is entirely non-toxic, low-production energy, 100% biodegradable material. Although there are an abundance of the material but storage of bales may require extra costs and effort to keep them dry.
- Kenaf wood core chips are another nontoxic insulating material made of natural, organic materials. The major disadvantage is the high cost per sq. ft per R-rating. Also, it must be treated with sodium hydroxide to manage moisture performance.
- Recycled Pet based insulation contains 100% recycled polyester and is made almost entirely from recycled plastic bottles. The technology can reduce the carbon footprint as well as show good insulating performance.
- One of the innovative ideas is to use recycled jeans and denim as insulation. The product usually is made of recycled fiber products and is treated with boric acid to serve as a fire retardant. Improvement is required to manage poor moisture barrier performance.
- Fiberglass contains recycled glass and shows extremely good insulating performance but due to the high energy-intensive manufacturing process, this is not a highly recommended sustainable alternative.
In spite of extensive research around multiple types of recycled and renewable insulating materials, the lack of overall performance including durability, moisture resistance as well as cost and energy efficiency make it a little difficult to come up in the market rapidly.
Innovative products launched by leading companies to address sustainability in the building insulation
The majority of the reason to move towards the green alternative is the sustainability requirement and reduce the environmental carbon footprint.
The leading insulation material players like Rockwool, Owens Corning, and Saint Gobain have been doing extensive research to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Rockwool a Danish multinational manufacturer of mineral wool products launched Comfortboard 80 which is a stone wool-based insulation made from natural stone with a minimum of 40% recycled content. The product can be applied to exterior continuous insulation.
- Saint Gobin discovers ISOVER Glass wool insulation. Mineral materials include recycled glass accounts for a minimum of 40% – and 100% bio-sourced binder. It is infinitely recyclable.
- PROPINK L77 LooseFill Insulation developed by Owens Corning made up of a new High-Performance Fiberizing Technology that effectively distributed thermal requirements with less glass material. The product utilizes f 50% recycled glass content.
Various players, start ups are emerging in the market, doing constant research activity to bring an innovative sustainable alternative to the consumer.
Denim Insulation developed by Bonded Logic Inc:
Bonded Logic Inc. markets and manufactures innovative thermal and acoustical insulation products. Bonded Logic’s UltraTouch™ Denim Insulation developed contains 80% post-consumer recycled natural fibres that provide maximum R-value performance.
Recycled PET based Insulating material developed by Thermafleece
Thermafleece one of the UK’s leading brands of natural and sustainable insulation has developed SupaSoft Recycled Plastic Insulation. SupaSoft is using recycled polyester fibres made from recycled plastic bottles to manufacture soft-touch loft insulation that’s safe and easy to install. SupaSoft contains no harmful chemicals or binders and is completely safe to handle. Converting plastic bottles into insulation helps divert many tonnes of waste plastic from landfill or incineration helping protect our environment.
Everuse provides Upcycled Insulating Materials
Dutch startup Everuse produces upcycled building materials EverUse® Insulation Board from cellulosic waste. The Insulation Board is a sturdy, resilient, 100% circular, flexible insulation mat made from cellulose waste streams from paper and cardboard.
Mycelium insulation panel developed by innovative Start up Biohm
Biohm’s mycelium is designed to replace carbon-intensive and toxic insulation boards with a high-performing natural bio-based alternative. Initial testing indicates that the mycelium panel is a highly effective thermal insulating product and has achieved thermal conductivity as low as 0.03W/m.K. it shows an acoustic absorption of at least 75% at 1000Hz (the typical frequency of road traffic noise). Also, It has demonstrated that they are at least as durable as conventional materials.


What are the drivers and challenges?
Drivers
- Sustainable and Non hazardous Materials: Demand for materials having a low carbon footprint and the reduced energy consumption is constantly raising. Unlike fibreglass, insulation materials like wool and cotton are safe to handle and cause no irritation to the skin or respiratory tract. Recycled content reduces the overall carbon footprint.
- Lower Manufacturing Costs: Insulation options like wool, shredded denim, and cork require very low amounts of energy to produce in comparison to fibreglass or styrofoam insulation. Saving energy during production means a reduction in harmful greenhouse gases.
- Health Benefits: Eco-friendly materials can control the moisture of your indoor environment.
Challenges
- Access to feedstock: The natural feedstock used in the insulation application is not widely available. The collection and transportation are costly affairs as well as not much organized.
- Lack of durability of the alternative materials: Durability, fire resistance, water vapour diffusion, and fungal resistance in particular for the best performing materials are the important factors that need to be investigated more. The natural origin material shows poor performance with respect to that behaviour.
- Contamination: Exposure to water and other contaminants can reduce the R-value, and may also give mould and or mildew nourishment and a place to propagate which ultimately leads to material degradation.
Conclusion
Insulation plays an important role in the construction industry in the minimization of operational energy consumption, and noise reduction. Currently, insulation is performed via mineral and fossil-derived materials, which require high manufacturing energy. Therefore attention has been paid to find out energy-efficient sustainable alternatives to address sustainability in the building insulation industry.
Insulating materials derived from natural resources have been identified as low-embodied energy materials that reduce energy use and greenhouse gas emissions. Among all the natural resource-based materials mineral wool and sheep wool shows exceptional insulating properties as well as durability. Other plant-based greens and sustainable insulation materials are extremely good in terms of low-carbon and positive-energy buildings but more research activity is required to bring them to full-scale commercial production level as these are inferior to properties like moisture absorption, durability, fire protection etc.
Subsequently, recycled materials such as recycled textiles, fibre, plastics, and glass wool have been identified as the best-in-class sustainable alternative. The use of these materials can reduce the carbon footprint, avoid landfilling as well as provide the required insulating performance over a long duration of time.
Due to low carbon emission while manufacturing and abundance of material availability, future evolution will be around renewable bio-based alternatives like mycelium-based insulation.
Drive sustainability in the building insulation industry with our expert guidance. Contact us today to learn how we can help you innovate and achieve your sustainability goals.
Need a thought partner?
Share your focus area or question to engage with our Analysts through the Business Objectives service.
Submit My Business ObjectiveOur Clients
Our long-standing clients include some of the worlds leading brands and forward-thinking corporations.
- © 2021 Cheers Interactive (India) Private Limited. All rights reserved. FutureBridge ® is a registered trademark of Cheers Interactive (India) Private Limited.




































