Advantages and disadvantages
- Optimized Production Schedules
AI-driven predictive maintenance data enables more accurate production planning, minimizing the impact of maintenance on overall output.
Proactively addressing potential equipment failures reduces unplanned downtime, ensuring continuous production and customer satisfaction.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan
By addressing issues before they escalate, predictive maintenance contributes to the longevity of production equipment.
Efficient scheduling and reduced downtime result in significant cost savings in terms of labor, materials, and energy.
Disadvantages:
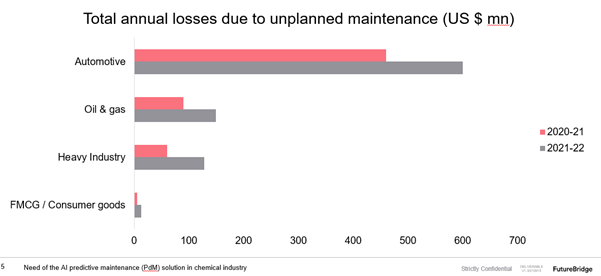
In a chemical plant, predicting failures is usually more difficult than it appears. Unscheduled downtime is typically concentrated in a few large events. That means there are too few datapoints for predictive maintenance systems to analyze from.
- Less time for arranging the alternatives.
Though it is possible to create models for predictive maintenance systems, usually it works on time perspectives which is too short. For example, predicting a part will fail in two days or two weeks is not useful in a plant where shutdowns take several days, and maintenance teams require months to plan interventions and source spare parts.
For installing predictive maintenance typically requires investments in sensors, data analytics software, and sometimes even IoT (Internet of Things) infrastructure. For many companies, the upfront costs can be quite high.
Implementing predictive maintenance requires integrating different technologies and systems, analyzing vast amounts of data, and retraining personnel. This can introduce complexities that not every organization is equipped to handle.