3 benefits brands can gain from smart packaging
 Food and Nutrition
Food and Nutrition
In the Internet of Things era, packaging needs to be smart and connected. It is expected that more than 10 million fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) will be interacted with throughout 2019, and the global market for smart packaging is expected to reach a volume of over $48 billion in 2024.
Smart packaging can be defined as providing enhanced functionality that can be divided into two submarkets: Active Packaging, which provides functionality such as moisture control, and Intelligent Packaging, which incorporates features that indicate the status or communicate product changes and other information.
This represents significant opportunities and benefits for brands who take advantage of what smart packaging has to offer. Let’s take a look at the 3 P’s of Smart Packaging; People, Planet and Profit.
1. People
Brands and their marketing teams are increasingly looking for novel ways to engage with consumers. As a result, more and more smart packaging technologies are stepping onto the scene to support their goals. From increased consumer interaction to providing a more informative overview of the product, smart technologies are improving consumer engagement in several ways.
Let’s take a look at some of the smart packaging technologies helping companies to enhance consumer engagement that are available today;
NFC Technologies
NFC, or near-field communication, is a communication technology and protocol that enables two electronic devices to communicate with each other and exchange information when they are near each other (within 4 centimeters). Someone using an NFC-enabled smartphone can interact with NFC tags or labels on a package or item with a simple tap.
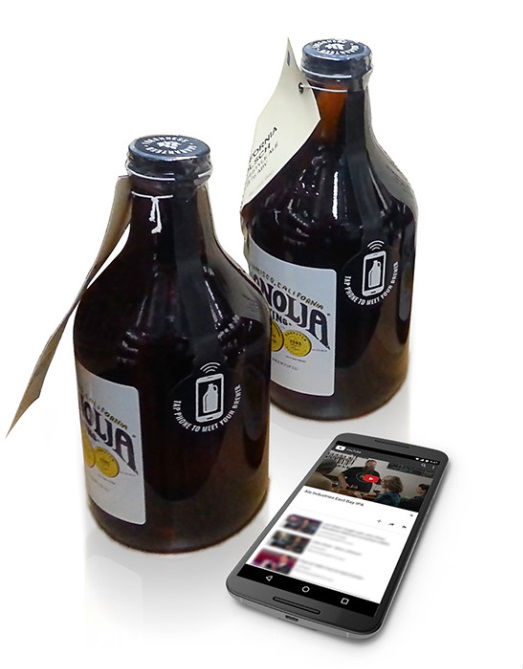 The Norwegian startup Thinfilm has developed several patents which utilize NFC tags for brand protection, consumer engagement, and supply chain insights. Thinfilm’s NFC OpenSense™ and SpeedTap solutions communicate wirelessly with NFC-enabled smartphones and can be applied to everyday objects via their CNECT cloud-based platform.
The Norwegian startup Thinfilm has developed several patents which utilize NFC tags for brand protection, consumer engagement, and supply chain insights. Thinfilm’s NFC OpenSense™ and SpeedTap solutions communicate wirelessly with NFC-enabled smartphones and can be applied to everyday objects via their CNECT cloud-based platform.
Thinfilms smart packaging technologies are focused primarily on the alcoholic beverage market. For example, Thinfilm and Hopsy, the USA’s first local craft beer marketplace and delivery service, have partnered to integrate NFC OpenSense™ tags into locally produced craft beer across the United States. NFC OpenSense™ tags will enable Hopsy’s partner breweries to engage with consumers and differentiate their brands. Using Thinfilm’s NFC technology, craft breweries can share their authenticity and craftsmanship stories directly with consumers.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality technologies allow companies to immerse the consumer within a specific branded experience. Augmenting the physical world with interesting and shareable content has been the focus of AR in experimental marketing.
Blippar, a UK startup founded in 2011, provides AR experiences to clients through two platforms. The first being the Blippar Studio which utilizes their engineers to create customized AR product experiences for their clients. Additionally, they have developed a simple AR creation tool called Blippbuilder which allows anyone to create their own AR campaigns with no coding or app set-up required.
Big players such as Kellogg’s, Cadbury and Nestle, have partnered with Blippar to produce interactive AR campaigns for their brands. For example, Blippar created a fun and shareable mobile campaign for Magnum. Consumers could tap on Magnum’s mobile banner ads to launch the AR experience without the need for a download. Once in the experience, users saw Magnum’s different custom toppings floating around them, which can then be selected to personalize their ideal ice cream. Customers could then redeem their creation from nearby stores shown in Google maps at a discount which met the brief of increasing the footfall for Magnums store and driving purchase intent.
2. Planet
One-third of all food produced around the world ends up in landfills annually, which amounts to nearly 1.3 billion tons of food get wasted. One key reason for this waste is the concern that surrounds use-by dates on the packaging, which were introduced as an important safety measure to prevent customers being sold and eating food that might be unsafe to eat. But more than a fifth of still-edible food is unnecessarily discarded due to date inaccuracies or confusion about what the dates actually mean.
Food waste is an environmental, social, and financial concern to the world but at the same time providing an opportunity for the packaging industry to develop smart packaging solutions. Intelligent packaging technologies such as Indicators and Modified Atmospheric Packaging (MAP) are being deployed by manufacturers to minimize unnecessary wastage as well as to improve the products overall safety and quality.
Indicators

Indicators determine the presence or absence of a substance, the extent of a reaction between different substances or the concentration of a particular substance. This information is visualized by direct changes, e.g., different color intensities. Depending on the indicator they are placed inside or outside of the package. The UK startup Mimica provides smart packaging solutions for the food and beverage industry by utilizing a smart label which is calibrated specifically for each food product and gives a tactile response – smooth when fresh and bumpy when the food is no longer safe for consumption. The label consists of a gelatin-based expiry indicator which deteriorates at the same rate as the packaged product, providing consumers with an accurate indication as to whether food is edible, or ready for the bin.
In December 2018, Danish dairy giant Arla picked up this smart technology for their milk bottles and is currently carrying out consumer tests in the UK in an attempt to understand consumer reaction. If successful, the Mimica Touch labels will be rolled out in supermarkets in the country later in the year, with the expectation of appearing elsewhere in Europe if all goes well.
Modified Atmospheric Packaging (MAP)
Modified Atmospheric Packaging (MAP) is a type of active packaging technology looking to extend the storage time of packaged food as well as maintain freshness, nutritional value, color and appearance of a food for a longer period. MAP is used for foods that are not sterile and whose enzymatic systems may still be operative. It alters the gaseous composition of the air present such as oxygen, nitrogen and carbon dioxide in a food package according to the desired profile.
Amcor is one of the bigger companies which develops smart packaging technologies and is a global leader in MAP solutions. Its product LifeSpan® adds value to a range of fruit and vegetable types by maintaining optimum quality throughout the distribution chain and allowing more cost effective and flexible storage and transport options. The fundamental purpose of LifeSpan® packaging is to extend the post-harvest storage life of fresh produce by slowing the ripening of the produce through MAP techniques.
3. Profit
Smart packaging is expected to continue to experience high growth in the coming years as it is viewed as an application that can create enormous value for a company. In 2015 smart packaging generated revenues of $23.5 billion and this is expected to grow by 11% annually, reaching $39.7 billion by 2020. Major players in the food and beverage industry are showing interest in this new area as a significant opportunity to generate and leverage data to make better business decisions and improve consumer loyalty. Overall, achieving a competitive return on investment.
Some of the technologies providing this new set of revenue streams include QR codes, RFIC, IoT and blockchain.
QR-code
QR-code is a type of 2D code that consists of black modules arranged in a square pattern on a white background. The information encoded can be made of any kind of data such as binary or alphanumeric. QR-codes are used to help consumers make informed purchase decisions through their smart phones as well as provide manufacturers with information on the products integrity, inventory management and new data insights across the entire supply chain.
ScanTrust, a Swiss startup founded in 2014, provides brands with smart packaging solutions for product authentication, supply chain traceability and consumer engagement. Their offerings include;
- Secure Graphic and QR code – secures a brands products and protect them against counterfeits
- Business Intelligence Dashboard – provides insights into your supply chain and customer profiles
- Blockchain – enhance product transparency and increase consumer trust using ScanTrust’s Blockchain connectors
Some of the players that have utilized ScanTrust smart packaging platform includes the major beverage producer ABInBev, Unilever, Abbott and DowDuPont.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
RFID tags, an intelligent packaging solution, uses a wireless radio wave to identify products through a chip embedded on the object. The tag chip contains a memory which stores a code and other variable information so that it can be read and tracked by RFID readers anywhere.
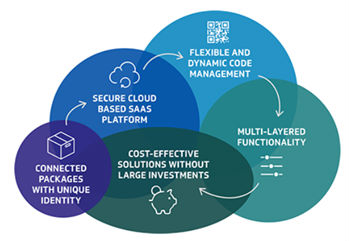 The Finnish startup Magic Add is creating the Internet of Packaging. Magic Add uses intelligent back-end technology to manage FMCG products along the entire supply chain. Each product has a machine-readable identity due to its adaptation to multiple coding systems: QR, RFID and NFD. Information about a single product is updated on their cloud platform and the platform uses blockchain to update and store code information securely on the cloud.
The Finnish startup Magic Add is creating the Internet of Packaging. Magic Add uses intelligent back-end technology to manage FMCG products along the entire supply chain. Each product has a machine-readable identity due to its adaptation to multiple coding systems: QR, RFID and NFD. Information about a single product is updated on their cloud platform and the platform uses blockchain to update and store code information securely on the cloud.
Since launching their product in 2011, Magic Add has partnered with leading packaging manufacturers such as Hutamaki, as well as global consumer brands including the major Nordic coffee producer Paulig.
Smart packaging is disrupting a once conventional industry
Previously just a delivery medium, packaging is rapidly becoming an active component of a product, enabling brands to engage with customers, reduce their negative environmental impact and monitor the integrity of their products.
Technologies in this space are driven primarily by small startups and their solutions must scale up to have a more dominant presence in the market. This is slowly changing as smart packaging technology providers lower cost and raise performance leading to a growing interest in this sector. In the near future, more and more companies in the food and beverage ecosystem will begin to uncover the significant opportunities and disruptive benefits that smart packaging can deliver.



 9 min read
9 min read
































